BUSINESS
& POLITICS IN THE WORLD
GLOBAL
OPINION REPORT NO. 642
Week: June 08 – June 14,
2020
Presentation: June 19, 2020
641-43-23/Commentary: 80% of Spaniards claim
to have enjoyed their home despite confinement
Indians
fear levels are increasing as India re-opens
Singaporeans
divided on tracking token
Talaat
Moustafa Group’s controversial advertisement leads to uplifts in brand
perception
34%
of Italians want to undergo the serological test
80%
of Spaniards claim to have enjoyed their home despite confinement
How
will Norwegians change behavior on the other side of the corona pandemic?
Half
of marketing decision-makers spending less money due to coronavirus
How
are parents coping with home schooling?
A
third of Brits want tighter rules on video game gambling
Will
Britons flock back to high street?
Over
a fifth of key workers lose income if they self-isolate
Canada's
support for Israel in the spotlight ahead of key UN vote
Unemployment
rose higher in three months of COVID-19 than it did in two years of the Great
Recession
#BlackLivesMatter
surges on Twitter after George Floyd’s death
A
majority of Americans say immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want
Amid
Slow Return to Workplaces, COVID-19 Precautions Abound
Social
Factors Most Challenging in COVID-19 Distance Learning
Awareness
of buy-now-pay-later services Afterpay and Zip soars to over 12.3 million
Australians
Do
wealthy adults expect COVID-19 to cause recession?
How
does COVID-19 spread? Global public belief in myths and theories
INTRODUCTORY NOTE
642-43-23/Commentary: 80% of Spaniards claim to have enjoyed their home despite confinement
According to a study carried out by YouGov for the ManoMano marketplace, Spaniards have focused their household chores on organization, order and DIY
32% of the respondents indicate that they prefer to exercise caution and get together with their family and friends at home
Two months of confinement have made Spaniards find their homes again and this is demonstrated by the study carried out by ManoMano.es, the leading DIY, home and garden marketplace, with the collaboration of the YouGov consultant, according to which 80% of Spaniards claim to have enjoyed their home during confinement . The reason? They have spent more time with their loved ones, and they have also taken advantage of their free time to make small reforms, tidy up and reorganize the house, and other tasks that previously, due to time, they could not carry out.
The study is published on the occasion of World DIY Day on May 24, and shows how the Spanish have made their home a more welcoming place during the quarantine. The order and organization have been the main activity as confirmed by the 72% of respondents. 31% have also been encouraged with DIY and have carried out small reforms, repairs, painted the walls, etc. And there are also 27% who have done DIY work (crafts, tutorials, ...) and 21% who have dedicated themselves to gardening and caring for plants.
The marketplace has noticed this. Demis Torres, Head of sales of Spain at ManoMano points out that “there has been an exponential increase in sales in recent weeks and our turnover has increased more than 250% in Spain compared to the same period in 2019. In fact, Among the most searched categories during the quarantine are interior furniture, outdoor furniture and sets, gardening tools, as well as interior and exterior paints, coinciding with the tasks that consumers have performed the most, according to the study. ”
By spending more time at home, it seems that the Spanish have cared more about her, and have enjoyed her even more. The main reason why respondents have enjoyed both of their homes during quarantine has been the share with your loved ones , especially households with children (51%) compared to households without minor (31%). Also because at home they feel more protected (18%) and because they have had more time to organize, organize and put it to their liking (15%).
In this first phase of lack of understanding, the priority continues to be to enjoy encounters with friends and family, as long as they are not very crowded. And although Spaniards feel like going outside, they prefer to act in a measured manner and enjoy the outdoors from home , organizing meetings at home (32%) or with family or friends (34%), especially outdoors free in the gardens, balconies and terraces, ahead of the 22% who prefer to stay in bars and restaurants.
The main reason is that the safety of diners prevails over anything, according to 44% of respondents, followed by 39% who want to make their closest friends enjoy their home, just as they have done in recent weeks.
(YouGov)
May 26, 2020
Source: https://es.yougov.com/news/2020/05/26/el-80-de-los-espanoles-afirma-haber-disfrutado-de-/
642-43-24: Country Profile/ Spain

SUMMARY
OF POLLS
ASIA
(India)
Indians fear levels are increasing as India re-opens
As India starts the process of re-starting the economy with ‘Unlock
1’, data from YouGov’s ongoing Covid-19 tracker shows an increasing number of
urban Indians are worried about losing their jobs due to the Coronavirus
outbreak. According to the tracker, 45% Indians said they were very or fairly
worried about job loss when we first surveyed them in early May. This coincides
with the time of ‘Lockdown 3.0’ in India. As the lockdown moved into its fourth
edition, the fear levels intensified, and towards the end of ‘Lockdown 4.0’ and
beginning of ‘Unlock 1’, 54% respondents said they are very or fairly worried
about losing their jobs. This is a total of 9% points increase over a period of
four weeks. The figure is much higher among people in their thirties, with 62%
of them feeling insecure about their jobs. (YouGov)
June 10, 2020
(Singapore)
Singaporeans divided on tracking token
Latest YouGov data reveals what Singaporeans think about the token,
and of the nation being the first in the world the world to roll out a wearable
device to track COVID-19. With an online petition gathering over 50,000
signatures so far, the tracking token appears to be quite a polarising topic.
In spite of the government reiterating that the token will not track one’s
location, Singaporeans remain divided on the issue. Over half (57%) are willing
and the under half (43%) are unwilling to wear / carry a tracking token.
Looking at the degree to which Singaporeans are willing, one in five (18%) are
very willing, two in five (39%) are somewhat willing, a quarter (26%) are
somewhat unwilling and one in six (17%) are very unwilling. (YouGov)
June 18, 2020
MENA
(Egypt)
Talaat Moustafa Group’s controversial advertisement leads to uplifts in
brand perception
Despite receiving backlash on social media, the overall sentiment
around the brand has improved following the launch of its new commercial. Community
real estate developer Talaat Moustafa Group (TMG) Holding has recently provoked
public outcry in Egypt, with the launch of their Madinaty TV commercial in May.
The three-minute video, released at the beginning of the Holy month of Ramadan,
features short clips focussing on residents highlighting their favourite things
about living in Madinaty - a gated community in New Cairo. Critics immediately
accused the advert of being insensitive and social media was flooded with memes
and comments calling out the provocative theme of class segregation. (YouGov)
June 09, 2020
EUROPE
(Italy)
34% of Italians want to undergo the serological test
More than one in 10 people in Italy suspect they have contracted
Covid-19, but for these people there has not been a certain diagnosis. Today,
as the emergency subsides, many would like to dispel any doubts with a
serological test. The serological tests are now available to the public and
allow you to detect infection by Covid-19 contracted in the past through the
detection of antibodies in the blood. Several researches, official and not suspect for months an underestimation of
Coronavirus cases all over the world, including Italy: the individual
experience of people confirms this. 12% of Italians today think they have
contracted the virus. (YouGov)
June 10, 2020
(Spain)
80% of Spaniards claim to have enjoyed their home despite confinement
According to a study carried out by YouGov for the ManoMano
marketplace, Spaniards have focused their household chores on organization,
order and DIY. 32% of the respondents indicate that they prefer to exercise
caution and get together with their family and friends at home. The study is
published on the occasion of World DIY Day on May 24, and shows how the Spanish
have made their home a more welcoming place during the quarantine. The order
and organization have been the main activity as confirmed by the 72% of
respondents. 31% have also been encouraged with DIY and have carried out small
reforms, repairs, painted the walls, etc. And there are also 27% who have done
DIY work (crafts, tutorials, ...) and 21% who have dedicated themselves to
gardening and caring for plants. (YouGov)
May 26, 2020
(Norway)
How will Norwegians change behavior on the other side of the corona
pandemic?
What happens when the coronary pandemic is over? We have taken a
closer look at how consumers view the future. The corona pandemic has created
changing and new consumption patterns, but when the pandemic is over will the
Norwegians' behavior be the same as before or will they have changed? We have
asked Norwegians how they view the future. Every third Norwegian does not
believe that their behavior will have changed as a result of the coronavirus.
Especially men are of this opinion (37% versus 26% of women). However, a larger
proportion of Norwegians (44%) disagree and believe that their behavior will be
different in the future. In general, many will support local businesses more,
spend less cash and buy more environmentally friendly products. (YouGov)
June 16, 2020
(UK)
Half of marketing decision-makers spending less money due to
coronavirus
Kraft Heinz and Procter & Gamble recently indicated that they
might increase their respective marketing spends in an attempt to build
“momentum” and invest in their brands during the COVID-19 lockdown. At a time
of widespread cost-cutting, job losses and reduced economic activity, it’s an
approach that might be considered unorthodox – especially given global budget
cuts that occurred as recently as August 2019. Data from YouGov Business
Omnibus suggests that firms which are increasing their marketing outlay are the
exception rather than the rule. In a recent poll of marketing decision-makers,
half (50%) said their spend had decreased with a third (35%) saying they were
spending “much less”. Only 13% are paying for more marketing and advertising.
(YouGov)
June 08, 2020
(UK)
How are parents coping with home schooling?
Two thirds of parents who are home schooling children during the
coronavirus lockdown are struggling to maintain discipline and motivation. Reception
and year one and six pupils returned to school last week, and YouGov data
suggests parents may have a new-found appreciation for the teaching profession.
Nearly three quarters of parents with school-age children (73%) have spent time
home schooling their kids during the coronavirus outbreak. Among this group,
two thirds said keeping their children disciplined and motivated was very (26%)
or fairly (39%) hard. The second most cited challenge was finding enough time,
with half of home schooling parents saying it has been very (17%) or fairly
(31%) hard. (YouGov)
June 08, 2020
(UK)
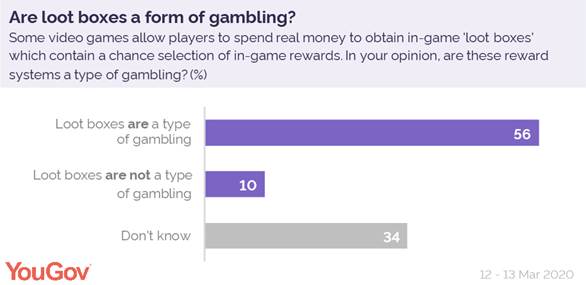
A third of Brits want tighter rules on video game gambling
Many Britons stuck inside on lockdown are turning to video games to
keep themselves and their children entertained. Many of these games allow
players to use real money to buy virtual items, or even to play games of chance
for virtual rewards. New YouGov research shows that most Brits want to see
changes in the law to protect gamers from what is, essentially, a form of
gambling. The “Loot Box” system, which is used in many popular games such as
Fifa and Fortnite as well as free-to-play mobile games, awards the player a
random in-game reward. These loot boxes are often brought with in-game
currencies paid for with real money – and half (56%) of Brits think that makes
them a type of gambling. (YouGov)
June 12, 2020
(UK)
Will Britons flock back to high street?
Today is a major milestone on the long road back to normality for
the UK, as non-essential shops open their doors for the first time since March
23rd. But with the COVID-19 pandemic still present, will shoppers be willing to
return to shopping in person? Of the high street shops opening today, clothing
stores are the place Brits will feel most comfortable returning (40%). But this
is some way off garden centres (64%) which opened on the 13th of May. These
take the top spot as the place Brits are most comfortable returning to,
possibly due to their open-aired nature. Another two fifths (40%) of Brits say
they would also be comfortable returning to indoor shopping centres and malls,
with 9% very comfortable doing so – however half (50%) of Brits say they
wouldn’t be comfortable heading into their local indoor shopping centre just
yet. (YouGov)
June 14, 2020
(UK)
Over a fifth of key workers lose income if they self-isolate
New YouGov data shows that 22% of key workers face some reduction
in their income if they self-isolate. This includes 6% who don’t get paid at
all, while 11% receive statutory sick pay (£95.85 per week). Additionally, 5%
receive more than statutory sick pay but less than their normal salary. Close
to a fifth (18%) of critical workers also miss out on pay if they have to
shield due to being in a high-risk group, including 7% who receive no income at
all. The actual numbers could be higher as over a fifth (22%) are
uncertain. Nearly half of essential
workers in sectors like delivery, transport and food (47%) report that they
would miss out on income if they were to self-isolate. (YouGov)
June 11, 2020
NORTH AMERICA
(Canada)
Canada's support for Israel in the spotlight ahead
of key UN vote
As Canada vies for UNSC seat, new survey
shows 74 percent of its citizens want country to oppose Israel annexation plan.
Most Canadians want Prime Minister Justin Trudeau's government to oppose
Israel's illegal plans to annex parts of the occupied West Bank, according to a
new poll released ahead of a vote on Canada's bid for a seat on the United Nations
Security Council (UNSC). The poll, conducted by EKOS Research Associates and
published on Tuesday, showed that three out of four Canadians want their
government to express opposition to Israeli annexation in some form, while 42
percent supported the use of economic or diplomatic sanctions against Israel.
(Al Jazeera)
June 17, 2020
(USA)
Americans’ views on World Health Organization
split along partisan lines as Trump calls for U.S. to withdraw
The World Health Organization, a
specialized agency of the United Nations, has historically served several
public health functions, including fighting communicable and non-communicable
diseases. It has played a high-profile role in addressing the global spread of
the coronavirus, which it characterized as a pandemic in early March. But in
mid-April, U.S. President Donald Trump ordered his administration to halt U.S.
funding of the organization, accusing it of making a series of consequential
mistakes in its handling of COVID-19. On May 29, Trump announced that he would
seek to terminate the country’s relationship with the WHO completely and
redirect funds toward other world public health needs. Amid scrutiny of the
WHO, here are key facts about the organization and how Americans see it.
(Pew Research Center)
June 11, 2020
(USA)
Unemployment rose higher in three months of
COVID-19 than it did in two years of the Great Recession
The COVID-19 outbreak and the economic
downturn it engendered swelled the ranks of unemployed Americans by more than
14 million, from 6.2 million in February to 20.5 million in May 2020. As a
result, the U.S. unemployment rate shot up from 3.8% in February – among the
lowest on record in the post-World War II era – to 13.0% in May. That rate was
the era’s second highest, trailing only the level reached in April (14.4%). The
rise in the number of unemployed workers due to COVID-19 is substantially
greater than the increase due to the Great Recession, when the number
unemployed increased by 8.8 million from the end of 2007 to the beginning of
2010. The Great Recession, which officially lasted from December 2007 to June
2009, pushed the unemployment rate to a peak of 10.6% in January 2010,
considerably less than the rate currently, according to a new Pew Research
Center analysis of government data. (Pew Research Center)
June 11, 2020
(USA)
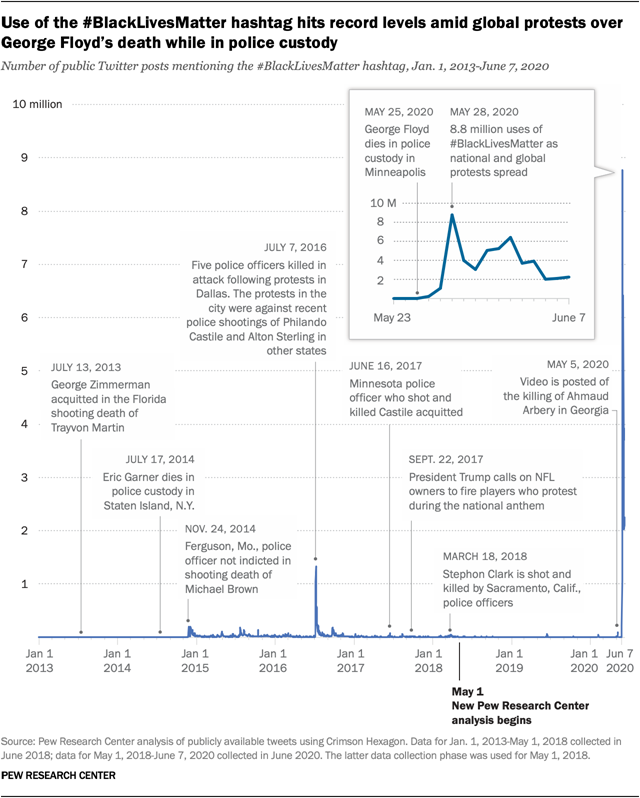
#BlackLivesMatter surges on Twitter after George
Floyd’s death
As nationwide protests continue over
police brutality and the death of George Floyd, the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag,
which is often used in connection with police-related deaths of black
Americans, has been used roughly 47.8 million times on Twitter – an average of
just under 3.7 million times per day – from May 26 to June 7, according to a
new Pew Research Center analysis of publicly available tweets. Public reactions to the death of Floyd –
an unarmed black man – on May 25 while in the custody of Minneapolis police
emerged quickly on Twitter. There were roughly 218,000 tweets containing the
#BlackLivesMatter hashtag the day after his death, when the first bystander
video was posted online. Once protests began in Minneapolis and spread across the
country and around the world, daily use of the hashtag passed 1 million on May
27. (Pew Research Center)
June 10, 2020
(USA)
A majority of Americans say immigrants mostly fill
jobs U.S. citizens do not want
Americans generally agree that immigrants
– whether undocumented or living legally in the country – mostly do not work in
jobs that U.S. citizens want, with a majority saying so across racial and
ethnic groups and among both political parties. This is particularly true when
it comes to undocumented immigrants. About three-quarters of adults (77%) say
undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want, while 21%
say undocumented immigrants fill jobs U.S. citizens would like to have,
according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted April 29 to May 5. Hispanics (88%) are most likely to say
undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want, with more
Hispanic immigrants than U.S.-born Hispanics saying so (94% vs. 82%). By
comparison, similar shares of white (75%) and black (71%) adults say the same.
(Pew Research Center)
June 10, 2020
(USA)
Hispanic women, immigrants, young adults, those
with less education hit hardest by COVID-19 job losses
The economic downturn caused by the
COVID-19 outbreak has been unsparing in its impact on the U.S. labor market.
The number of employed workers fell by 24.7 million from February to April 2020
as the outbreak shuttered many parts of the economy. With the easing of
government-mandated closures in recent weeks, employment picked up by 4.1
million from April to May. But overall, job losses remain sizable, with
employment decreasing by 20.6 million (or 13%) from February to May. The
downturn has affected some Americans more than others, particularly Hispanic
women, immigrants, young adults and those with less education. The decrease in
employment in the first three months of the COVID-19 recession is more than
double the decrease effected by the Great Recession over two years. From the
end of 2007 to the end of 2009, U.S. employment fell by 8.0 million, or 5%. (Pew
Research Center)
June 09, 2020
(USA)
Amid Slow Return to Workplaces, COVID-19
Precautions Abound
As state economies across the U.S. are
gradually reopening, workers are slowly returning to their workplaces, yet it
is far from business as usual for most. Majorities of workers whose workplaces
have employees on-site report that their employers are taking precautions to
keep people from catching or spreading the coronavirus. These safeguards
include new or more frequent cleaning procedures at work, a measure 69% of
workers report their employer is "always" taking. Additionally, 58%
say their employer is always providing personal protective equipment, such as
masks, gloves or face shields, and 54% say employers are enforcing a six-foot
distance between employees and customers or other employees. Fewer, 41%, say
their employers are always screening employees for cough or fever. (Gallup USA)
June 08, 2020
(USA)
Social Factors Most Challenging in COVID-19
Distance Learning
The 2019-2020 academic year is ending in
a way no one could have imagined, with classes being taught virtually and many
parents serving as their child's primary instructor as schools are closed
because of the coronavirus pandemic. Asked to rate the various challenges
they've faced with remote learning, parents are more likely to identify
difficulties they or their child has had in adjusting to virtual learning as
major challenges than technical or resource issues. Forty-five percent say
their children being separated from classmates and teachers has been a major
challenge for their family, and 44% say the same about their child's attention
span and motivation. Also, 43% of working parents say balancing a job and
helping kids with school has been a major challenge for them. (Gallup USA)
June 12, 2020
AUSTRALIA
Awareness of buy-now-pay-later services Afterpay
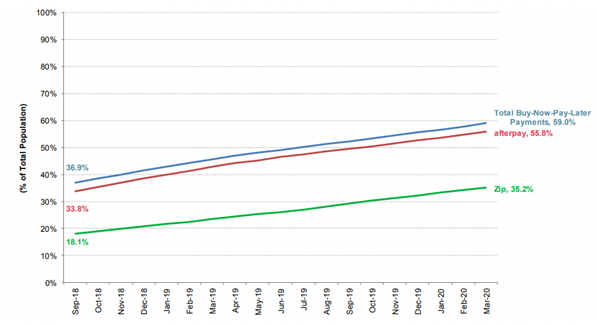
and Zip soars to over 12.3 million Australians
Afterpay is the clear market leader with
a majority of 55.8% of Australians aware of the service in the year to March
2020, up by 22% points since September 2018. Main rival Zip is also making a
significant impression on the Australian marketplace with over a third of
Australians (35.2%) now aware of Zip – almost doubling awareness of the service
in only 18 months. The rising awareness of buy-now-pay-later services comes as
the share prices of Afterpay, Zip and smaller rivals has soared during the
COVID-19 induced shut-downs. The Afterpay share price increased by over 500%
since a low of only $8 in late March and the share price of Zip was up over 50%
last week alone. (Roy Morgan)
June 09, 2020
MULTICOUNTRY STUDIES
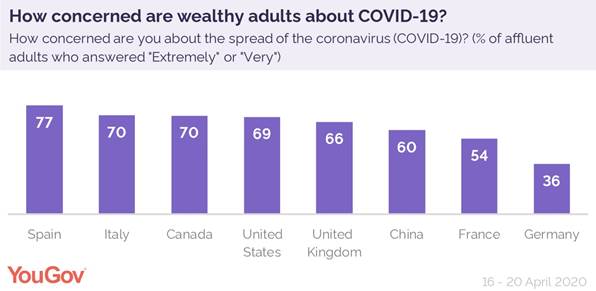
Do wealthy adults expect COVID-19 to cause recession?
YouGov Affluence Perspective polling of wealthy adults* around the
world reveals what concerns them most about the COVID-19 pandemic: looming
recession, and whether local economies will be able to survive. Concern over
the spread of the virus varies greatly across the countries examined in our
latest survey, with European nations particularly split. At the top end are
wealthy adults in Spain and Italy, 77% and 70% of whom respectively say they
are either extremely or very concerned about the spread of COVID-19. At the other end of the spectrum are France and Germany, where just
54% and 36% of wealthy adults respectively say they are concerned. The UK sits
somewhere in the middle, with two thirds (66%) of wealthy adults (those who
have a household income of £100,000 or over) being concerned, similar to the US
(69%). (YouGov)
June 11, 2020
How does COVID-19 spread? Global public belief in myths and theories
In global poll of nearly 16,000 people conducted from May 28 to 31,
more people believe COVID-19 can live up to three days on surfaces over all
other theories presented with a majority of respondents saying this is true in
11 of the countries. People in Canada and the United Kingdom (69%), Australia
(66%), Spain and Brazil (61%) are most likely to believe this, while those in
China (32%), India (26%), Germany and South Korea (25%) and Italy (24%) are
most likely to say it’s false. But at the same time, people are more divided on
whether COVID-19 can be spread by boxes and packages sent from other countries
where the virus is present. Respondents in emerging markets of India (54%),
South Africa (50%), Brazil (45%) and China (42%) are most likely to believe
this, while those in Italy (66%), Russia (61%) and Germany (55%) are most likely
to disagree. (Ipsos MORI)
June 11, 2020
ASIA
642-43-01/Poll
Indians fear levels are increasing as India re-opens
From fear of the coronavirus disease to losing their jobs, YouGov’s global COVID-19 tracker shows that Indians are getting increasingly anxious about both health and the economy
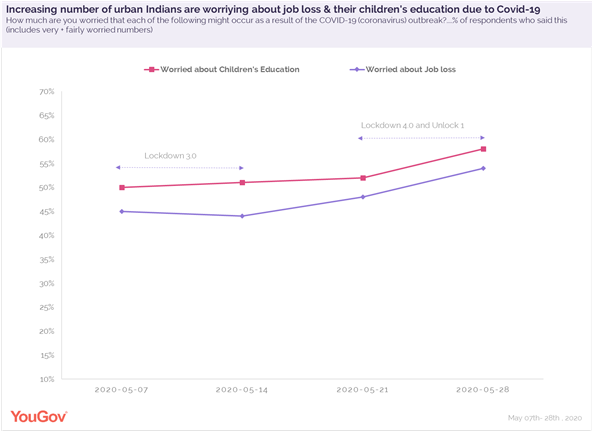
As India starts the process of re-starting the economy with ‘Unlock 1’, data from YouGov’s ongoing Covid-19 tracker shows an increasing number of urban Indians are worried about losing their jobs due to the Coronavirus outbreak. According to the tracker, 45% Indians said they were very or fairly worried about job loss when we first surveyed them in early May. This coincides with the time of ‘Lockdown 3.0’ in India. As the lockdown moved into its fourth edition, the fear levels intensified, and towards the end of ‘Lockdown 4.0’ and beginning of ‘Unlock 1’, 54% respondents said they are very or fairly worried about losing their jobs. This is a total of 9% points increase over a period of four weeks. The figure is much higher among people in their thirties, with 62% of them feeling insecure about their jobs.
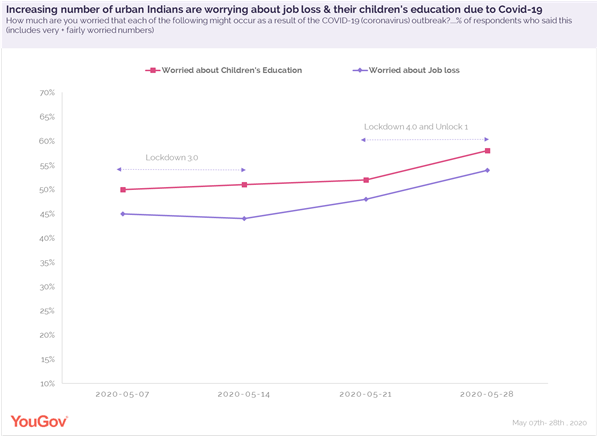
For the same period, worry about their children’s education has also witnessed an upward swing. The shift to remote learning through online classes and the uncertainty around reopening of schools could be a reason for parents getting anxious about the future of their child’s education.
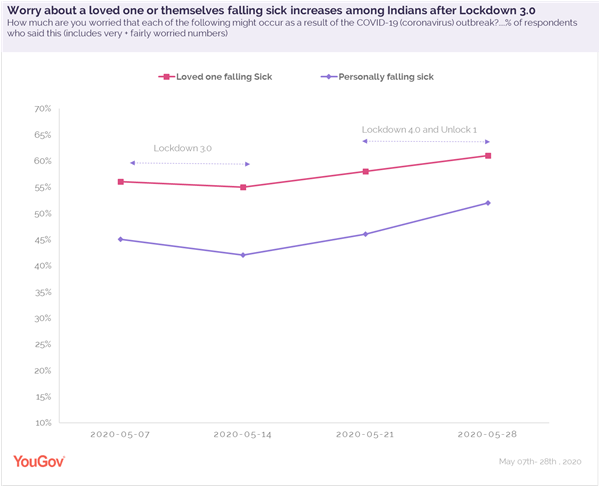
As people stayed at home and practised social distancing in lockdown 3.0 (early May), less than half were worried about falling sick or dying because of the virus. However, as the lockdown was extended, followed by the reopening of public places and offices, worry among residents seems to have increased and 52% now said they are very or fairly worried in this regard. Similarly, concern about loved ones feeling unwell or dying due to the virus has also seen an escalation from 56% to 61% now. Worry is considerably higher among tier-1 city residents as compared to people in tier-3 cities (66% vs 57%).
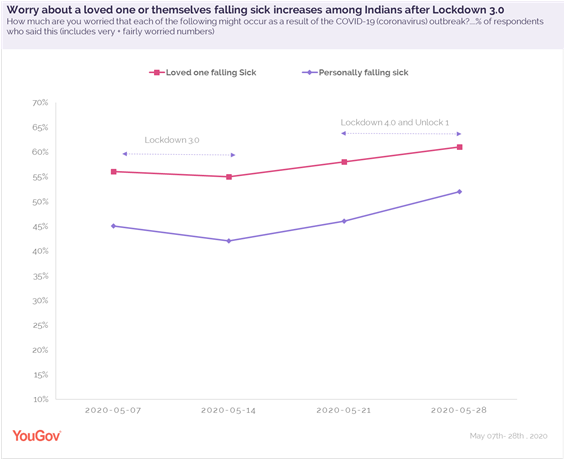
Comparatively, concern over other possible impacts of the disease, such as effect on their finances and a long-lasting harm to the society have seen a marginal difference over the weeks.
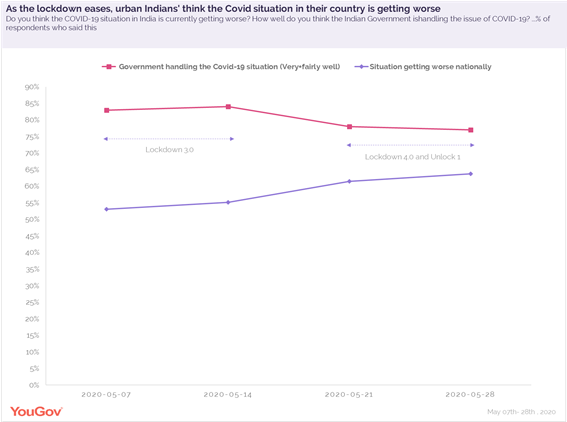
At an overall level, Indians’ confidence in the government handling the Covid crisis has plummeted over the past few weeks. 83% respondents said the government is handling the crisis very or fairly well when we first surveyed them in early May. Now, this number has reduced to 77% at the end of lockdown 4.0, a fall of 6% points. Among the different regions, confidence is the lowest among people in West India compared to the rest - at 70% (very or fairly well handling of the crisis).
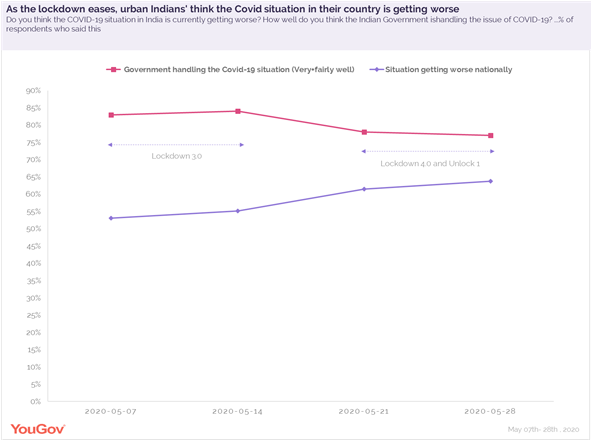
Faith in national Covid recovery also seems to have dwindled over the weeks. The data shows the number of people who said the situation in their country is getting worse has increased from 53% in the first wave of the survey (early May) to 64% in the fourth wave (early June). This marks an increase of 11% points.
YouGov will continue tracking public perception around the virus outbreak in the weeks to come.
(YouGov)
June 10, 2020
Source: https://in.yougov.com/en-hi/news/2020/06/10/indians-fear-levels-are-increasing-india-re-opens/
642-43-02/Poll
Singaporeans divided on tracking token
Almost half trust the government with their private data
In the continuous battle to curb the spread of COVID-19, the Singaporean government intends to roll out a tracking token, a small device that people can carry around in their bag or token. Latest YouGov data reveals what Singaporeans think about the token, and of the nation being the first in the world the world to roll out a wearable device to track COVID-19.
With an online petition gathering over 50,000 signatures so far, the tracking token appears to be quite a polarising topic. In spite of the government reiterating that the token will not track one’s location, Singaporeans remain divided on the issue. Over half (57%) are willing and the under half (43%) are unwilling to wear / carry a tracking token. Looking at the degree to which Singaporeans are willing, one in five (18%) are very willing, two in five (39%) are somewhat willing, a quarter (26%) are somewhat unwilling and one in six (17%) are very unwilling. Those over the age of 55 are the most willing to carry a tracking token and those aged 35 to 44 are the least willing (61% vs. 52%). Women are also more willing to carry a token than men (58% vs. 55%).
The biggest issue Singaporeans have with the token is privacy infringement, with three in five (58%) selecting it as a concern. This is followed by other concerns like inconvenience (43%), concerns about user-friendliness (27%), not thinking it would be effective (20%) and other reasons (2%). One in seven (14%) have no concerns with the token.
Almost half of Singaporeans (45%) trust the government with their private data, but this differs greatly between those are and are not willing to wear the token. For those who are willing to wear a token, almost two thirds (64%) trust the government with their data, but amongst those who aren’t willing to wear one, this drops to one in five (20%).
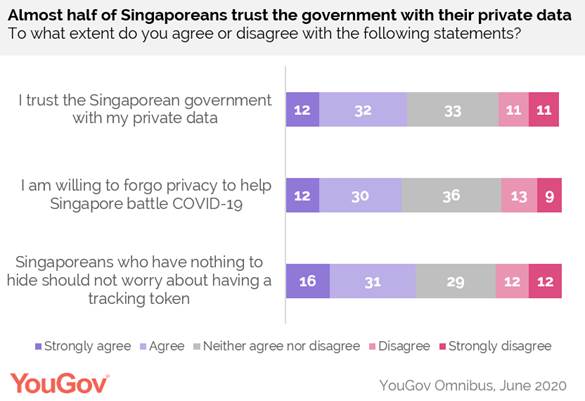
Two in five (42%) agree with the statement that they are willing to forgo privacy to help the nation battle COVID-19. One in five (22%) disagree and a significant amount are undecided (36%). Again, this differs greatly between those who are willing and not willing to carry a token (62% vs. 15%). Almost half (47%) agree with the statement that Singaporeans who have nothing to hide should not worry about having a token. Older Singaporeans (those aged 55 and above) are most likely to agree with this statement, while Singaporeans aged 25 to 34 are the least likely to agree (52% vs. 41%).
Jake Gammon, Head of Omnibus at YouGov Asia Pacific commented: “Though it’s been made clear the tracking tokens are purely for tracking the virus and not individuals, our data shows that they still remain a polarising topic. It is natural that privacy is first thing that comes to mind, but not everyone agrees on how much of their privacy they are willing to give up.”
(YouGov)
June 18, 2020
Source: https://sg.yougov.com/en-sg/news/2020/06/18/singaporeans-divided-tracking-token/
MENA
642-43-03/Poll
Talaat Moustafa Group’s controversial advertisement leads to uplifts in brand perception
Despite receiving backlash on social media, the overall sentiment around the brand has improved following the launch of its new commercial
Community real estate developer Talaat Moustafa Group (TMG) Holding has recently provoked public outcry in Egypt, with the launch of their Madinaty TV commercial in May. The three-minute video, released at the beginning of the Holy month of Ramadan, features short clips focussing on residents highlighting their favourite things about living in Madinaty - a gated community in New Cairo.
Critics immediately accused the advert of being insensitive and social media was flooded with memes and comments calling out the provocative theme of class segregation. Viewers described the commercial as wealth flaunting and boastful, exposing the hostility between classes in Egypt.
Indeed, recent data from YouGov BrandIndex confirms the “noise” the campaign has created, with Attention (hearing positive or negative buzz about the brand) increasing 18.5 points by the end of May. Ad Awareness and Word of Mouth for Talaat Moustafa also both increased significantly in May, showing residents of Egypt are not only noticing the advert, they are also discussing it.
Interestingly though, despite the criticisms and negative comments surrounding the commercial online, overall sentiment towards the brand actually improved. The proportion of respondents hearing something positive about the brand increased by 15% throughout May, compared to a 4% increase in the proportion hearing something negative about Talaat Moustafa.
It is therefore not so surprising to learn among the general population in Egypt the campaign has had a positive impact on brand perceptions of Talaat Moustafa. As well as raising the brand’s profile (Awareness on BrandIndex tracking around 70% at the end of May, compared to 65% at the end of April), the campaign appears to have had a significant impact on consumers’ Quality perceptions, as well as increasing Recommendation and Reputation metrics.
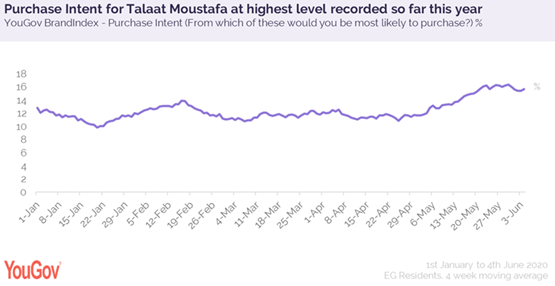
YouGov brand tracking data also underlines how successful the brand’s new advertising campaign has been in terms of shifting consumers’ purchasing intentions. May results show Consideration and Purchase Intent were both at the highest level recorded so far this year indicating that despite the controversy from some quarters, the public continue to be aspirational, with an increasing number setting their sights on Talaat Moustafa communities.
This advert and the impact it has had lends weight to the notion ‘there is no such thing as bad publicity’, with BrandIndex data confirming the success not only in terms of cut through, but also in terms of sentiment towards Talaat Moustafa.
(YouGov)
June 09, 2020
Source: https://mena.yougov.com/en/news/2020/06/09/talaat-moustafa-groups-controversial-advertisement/
EUROPE
642-43-04/Poll
34% of Italians want to undergo the serological test
More than one in 10 people
in Italy suspect they have contracted Covid-19, but for these people there has
not been a certain diagnosis. Today, as the emergency subsides, many would
like to dispel any doubts with a serological test.
The serological tests are now available to the public and allow you to detect infection by Covid-19 contracted in the past through the detection of antibodies in the blood. Several researches, official and not suspect for months an underestimation of Coronavirus cases all over the world, including Italy: the individual experience of people confirms this. 12% of Italians today think they have contracted the virus.
|
More than 1 in 10 people
in Italy suspect they have contracted Covid-19. |
|
Which
of the following options describes your personal Covid-19 situation? |
On a national scale, 5% of people have already taken the test, but 34% intend to do it in the future. The percentage rises to 52% if instead you look at the group of people who instead thinks they have suffered from undiagnosed Covid-19 infection: in addition, 2 out of 10 in this group have already taken the test.
What are the opinions on the
test, what are the reasons for taking it or not?
|
5% of Italians have
already undergone a serological test, and over a third will do so in the
future. |
|
Have you undergone Covid-19 serological tests? | Base : 1038 Italians 18+ |
At a national level, the number of people who do not intend to undergo the serological test is roughly equivalent to what they want to do. In the first group, 28% think it is currently unreliable, i.e. subject to false positive or false negative. A fourth, on the other hand, considers it an unnecessary medical examination (25%). The most striking difference is the thought that the presence of antibodies detected by the test protects or not from future infections, an aspect of which we are not yet sure.
A quarter (24%) of the disinterested think that "even in the case of a positive result (presence of antibodies) immunity is not guaranteed". On the other hand, 49% of people who want to undergo serology hope to be protected from future infections if they have already contracted the virus, and want to make sure of it by undergoing the test.
The idea that a positive result can protect against a second infection is
widespread nationwide. In fact, half the people say that "If a serological test confirmed that I have
already contracted Covid-19 in the past, I would feel more relaxed today" (53%).
Regardless of its clinical significance, most Italians believe that serological
tests should be offered free of charge to everyone (83%), or that even the
entire population should be tested.
Most of the Italians
appreciate the hypothesis of a health passport, especially in the south and
islands
In recent weeks, some regions, especially those with low contagion, have discussed the need to ensure that those who enter their territory are not sick of Covid-19. The health passport has become a controversial but also contested idea, but the opinion of Italians is multifaceted, especially on its application.
Half (52%) would agree that it was used to guarantee access to Italy from abroad . Consent gradually decreases if the certificate is used to leave Italy (47%) , and even more when it comes to travel between Italian regions (41%) .
|
The Italians say yes to a
hypothetical health passport , above all to make sure that those
who enter Italy are not positive. |
|
The Health Passport is a medical document that certifies the absence of Covid-19 infection, and which could be used to guarantee the movement of people. To what extent do you agree or disagree with the health passport to ensure the mobility of people between the regions of Italy / enter Italy / leave Italy? | Base : 1038 Italians 18+ |
The situation is uneven if the Italians are divided according to the area in which they reside. In fact, the need for certainties is inversely proportional to the rate of contagion observed in your region: the population of the south and the islands, which has been the least affected in the country but also has a health system most at risk in the event of an emergency, is much more conducive to controls at all levels, both inside and outside Italy.
(YouGov)
June 10, 2020
Source: https://it.yougov.com/news/2020/06/10/Sierologico-covid/
642-43-05/Poll
80% of Spaniards claim to have enjoyed their home despite confinement
According to a study carried out by YouGov for the ManoMano marketplace, Spaniards have focused their household chores on organization, order and DIY
32% of the respondents indicate that they prefer to exercise caution and get together with their family and friends at home
Two months of confinement have made Spaniards find their homes again and this is demonstrated by the study carried out by ManoMano.es, the leading DIY, home and garden marketplace, with the collaboration of the YouGov consultant, according to which 80% of Spaniards claim to have enjoyed their home during confinement . The reason? They have spent more time with their loved ones, and they have also taken advantage of their free time to make small reforms, tidy up and reorganize the house, and other tasks that previously, due to time, they could not carry out.
The study is published on the occasion of World DIY Day on May 24, and shows how the Spanish have made their home a more welcoming place during the quarantine. The order and organization have been the main activity as confirmed by the 72% of respondents. 31% have also been encouraged with DIY and have carried out small reforms, repairs, painted the walls, etc. And there are also 27% who have done DIY work (crafts, tutorials, ...) and 21% who have dedicated themselves to gardening and caring for plants.
The marketplace has noticed this. Demis Torres, Head of sales of Spain at ManoMano points out that “there has been an exponential increase in sales in recent weeks and our turnover has increased more than 250% in Spain compared to the same period in 2019. In fact, Among the most searched categories during the quarantine are interior furniture, outdoor furniture and sets, gardening tools, as well as interior and exterior paints, coinciding with the tasks that consumers have performed the most, according to the study. ”
By spending more time at home, it seems that the Spanish have cared more about her, and have enjoyed her even more. The main reason why respondents have enjoyed both of their homes during quarantine has been the share with your loved ones , especially households with children (51%) compared to households without minor (31%). Also because at home they feel more protected (18%) and because they have had more time to organize, organize and put it to their liking (15%).
In this first phase of lack of understanding, the priority continues to be to enjoy encounters with friends and family, as long as they are not very crowded. And although Spaniards feel like going outside, they prefer to act in a measured manner and enjoy the outdoors from home , organizing meetings at home (32%) or with family or friends (34%), especially outdoors free in the gardens, balconies and terraces, ahead of the 22% who prefer to stay in bars and restaurants.
The main reason is that the safety of diners prevails over anything, according to 44% of respondents, followed by 39% who want to make their closest friends enjoy their home, just as they have done in recent weeks.
(YouGov)
May 26, 2020
Source: https://es.yougov.com/news/2020/05/26/el-80-de-los-espanoles-afirma-haber-disfrutado-de-/
642-43-06/Poll
How will Norwegians change behavior on the other side of the corona pandemic?
What happens when the
coronary pandemic is over? We have taken a closer look at how consumers
view the future.
The corona pandemic has created changing and new consumption patterns, but when the pandemic is over will the Norwegians' behavior be the same as before or will they have changed? We have asked Norwegians how they view the future.
Every third Norwegian does not believe that their behavior will have changed as a result of the coronavirus. Especially men are of this opinion (37% versus 26% of women). However, a larger proportion of Norwegians (44%) disagree and believe that their behavior will be different in the future.
In general, many will support local businesses more, spend less cash and buy more environmentally friendly products.
Nearly 6 in 10 (57%) will do more to support local businesses / purchase local products. Most women (62%) agree with this.
The share of cash has been declining in Norway for many years, and today is around two per cent . And with the corona pandemic, Norway is perhaps even faster on its way to the cashless society. 4 out of 10 (41%) agree that they will use cash to a lesser extent in the future.
3 out of 10 will to a much greater extent buy environmentally friendly / sustainable products as a result of the corona virus. This is especially the case for women (36%) and young people aged 18-29 (35%).
1 in 4 (25%) will use online shopping / delivery to a much greater extent. Especially the 18-39 year olds will use online shopping more (36%). However, half of Norwegians (52%) will no longer use online shopping as a result of the coronavirus.
About the survey
The survey is part of YouGov's ongoing coronavirus tracking survey and is based on interviews with 2038 Norwegians. The sample is nationally representative of persons aged 18+ and was conducted in the YouGov panel from 18 to 22 May 2020.
(YouGov)
June 16, 2020
Source: https://yougov.no/news/2020/06/10/hvordan-vil-nordmenn-endre-atferd-pa-den-anden-sid/
642-43-07/Poll
Half of marketing decision-makers spending less money due to coronavirus
Spending on direct
marketing, events and sales promotions slashed as companies cut costs during
COVID-19 crisis
Kraft Heinz and Procter & Gamble recently indicated that they might increase their respective marketing spends in an attempt to build “momentum” and invest in their brands during the COVID-19 lockdown. At a time of widespread cost-cutting, job losses and reduced economic activity, it’s an approach that might be considered unorthodox – especially given global budget cuts that occurred as recently as August 2019.
Data from YouGov Business Omnibus suggests that firms which are increasing their marketing outlay are the exception rather than the rule. In a recent poll of marketing decision-makers, half (50%) said their spend had decreased with a third (35%) saying they were spending “much less”. Only 13% are paying for more marketing and advertising.
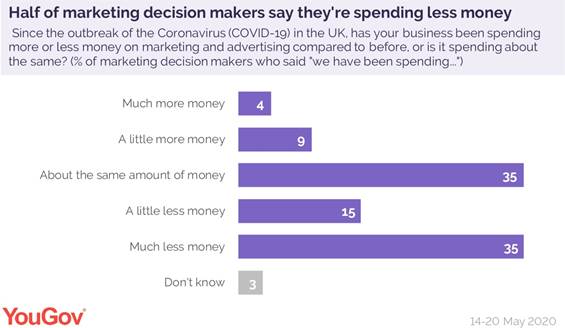
Two-thirds (65%) of decision-makers surveyed said their priorities have changed as a result of the pandemic, with three in ten (30%) saying they have been significantly altered. In terms of how this has changed their day to day marketing, half (50%) of those who are spending less have seen cuts to events – unsurprisingly, given the government’s moratorium on large gatherings – and direct marketing (52%), while 42% have limited spending on sales promotions. The latter two activities may be declining in tandem with consumer confidence; if people are less optimistic about their financial situation, they’re less likely to embrace the hard sell. Two in five of these marketing decision-makers (40%) are limiting their digital activities while 37% have reduced main media advertising.
When asked why their companies are spending less, over half (53%) of those who’ve seen budget cuts cite reduced spending across the business due to COVID-19, 37% say marketing’s resources have been redistributed to other parts of the business, and a fifth (19%) say the marketing team has been specifically targeted for cuts.
Marketing decision-makers also report some change to the performance of their campaigns. Three in ten (29%) say they’ve been less effective during the coronavirus outbreak, while only 17% have taken advantage of the new normal and seen an improvement in campaign performance. A third (35%) have noticed no difference and a fifth (20%) claim they don’t know either way.
(YouGov)
June 08, 2020
642-43-08/Poll
How are parents coping with home schooling?
Two thirds of parents who are home schooling children during the coronavirus lockdown are struggling to maintain discipline and motivation
Reception and year one and six pupils returned to school last week, and YouGov data suggests parents may have a new-found appreciation for the teaching profession.
Nearly three quarters of parents with school-age children (73%) have spent time home schooling their kids during the coronavirus outbreak. Among this group, two thirds said keeping their children disciplined and motivated was very (26%) or fairly (39%) hard.
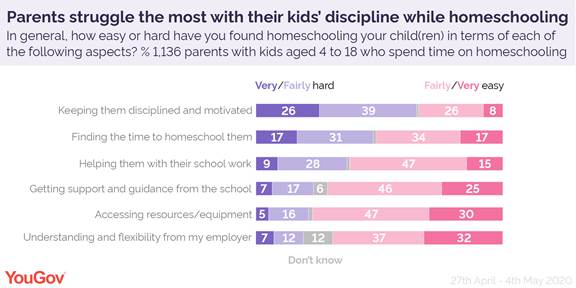
The second most cited challenge was finding enough time, with half of home schooling parents saying it has been very (17%) or fairly (31%) hard.
Similarly, having to step in as a teacher after decades away from school books has been challenging for 35% of home schooling parents, including 9% who say it is very hard.
Some have also struggled to get support from schools (24%), accessing resources and equipment such as laptops (21%) and being shown understanding from their employer (19%).
Middle-class parents report better access to support from schools
Several experts and commentators, including the head of Ofsted Amanda Spielman, have expressed concerns that home schooling will disadvantage students from poorer backgrounds. While this is a complicated issue, the data does reveal two interesting findings.
Firstly, parents in the C2DE social group, who tend to work in manual professions, have spent more time home schooling their children - at an average of 2.7 hours per day. Among ABC1 parents, who are often professionals, this figure is 2.5.
Another YouGov survey shows that higher numbers of ABC1 employees are working from home, while C2DE workers are more likely to have been furloughed during the lockdown. The numbers suggest the latter group have been in a better position to spend time home schooling their children.
Secondly, home schooling C2DE parents are more likely to report that they’ve found helping their children with schoolwork hard (40% compared with 35% of ABC1s). But it’s a modest gap. What’s more striking are the differing levels of support that ABC1 and C2DE parents say they have received from their child’s school.
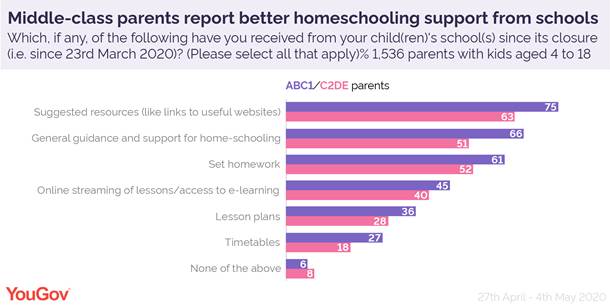
Two thirds ABC1 parents with kids of school-age (66%) said they have received general guidance and support for home schooling, such as information packs and having access to teachers, compared with 51% of C2DE parents. This was the most significant difference, at 15 percentage points.
The second largest difference was in teachers sharing useful resources (75% of ABC1 parents received this versus 63% of C2DEs). Providing set homework (61% versus 52%) and timetables (27% versus 18%) came third.
In every instance that we asked about, ABC1 parents were more likely to say they had received this form of support.
A small minority of parents with children of school-age did not receive any support or materials (7%).
Fathers have higher expectations but spend less time home schooling
Fathers are more likely to say their children should do the same amount of work at home that they would do in school. Just under two thirds of fathers with school-age kids (64%) say it’s very (23%) or fairly (40%) important. In contrast, this figure is lower among mothers at 55%, including 19% who say it’s very important.
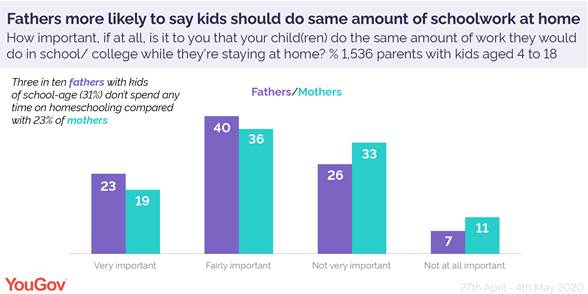
But while men may have higher expectations, they tend to do less of the actual teaching: 31% of fathers with school-age kids have not spent any time home schooling them, compared to 23% of mothers.
During lockdown mothers report that they’ve spent on average 2.7 hours daily home schooling. Among fathers this figure is 2.4 hours. And they reported feeling more pessimistic (28%) about being able to cope with the demands of home schooling than fathers (18%).
Among home schooling parents who work full-time, a higher number of women (24%) than men (18%) also said they found it hard because their employer lacked understanding and flexibility.
(YouGov)
June 08, 2020
642-43-09/Poll
A third of Brits want tighter rules on video game gambling
Systems that allow players
to spend real money for randomised in-game rewards should be subject to
gambling rules, say Brits
Many Britons stuck inside on lockdown are turning to video games to keep themselves and their children entertained. Many of these games allow players to use real money to buy virtual items, or even to play games of chance for virtual rewards. New YouGov research shows that most Brits want to see changes in the law to protect gamers from what is, essentially, a form of gambling.
The “Loot Box” system, which is used in many popular games such as Fifa and Fortnite as well as free-to-play mobile games, awards the player a random in-game reward. These loot boxes are often brought with in-game currencies paid for with real money – and half (56%) of Brits think that makes them a type of gambling.
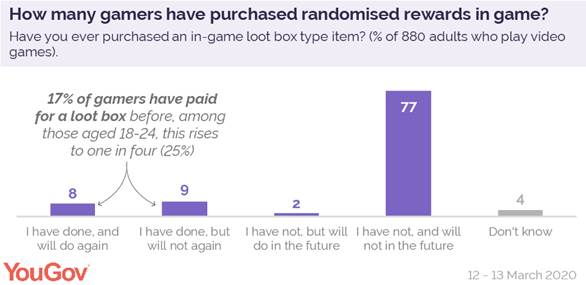
Overall one-in-six (17%) British gamers say they’ve spent money on loot box style systems in video games, rising to a quarter (25%) of gamers aged from 18 to 24.
But they do not seem to be a common repeat purchase, however, as only half of gamers who have used loot box systems (8% of gamers overall) say they would do so again.
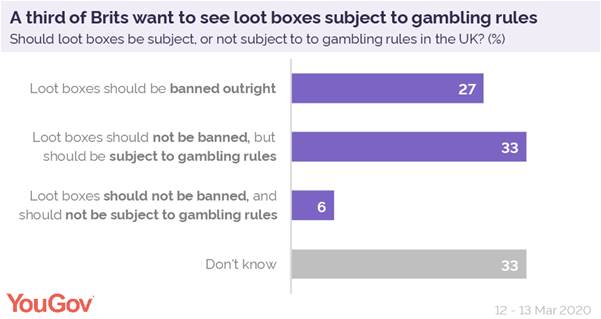
Given the popularity of video games among children [link to matt smith story], games featuring loot box systems were also accused of exploiting children by MPs last year. Other countries such as Belgium have gone as far to ban loot boxes outright – and six-in-ten (60%) Brits want to see the regulations imposed on similar systems here in the UK.
A quarter of Brits (27%) want to see the randomised loot system banned from video games outright, and another 33% want to see the systems subject to gambling rules. Only 6% of Brits think the systems should continue unregulated.
(YouGov)
June 12, 2020
Source: https://yougov.co.uk/topics/media/articles-reports/2020/06/12/loot-boxes-banned-uk
642-43-10/Poll
Will Britons flock back to high street?
Shops are reopening today after
months of lockdown, but our data shows that Britons are cautious about
returning
Today is a major milestone on the long road back to normality for the UK, as non-essential shops open their doors for the first time since March 23rd. But with the COVID-19 pandemic still present, will shoppers be willing to return to shopping in person?
Where do Brits feel
comfortable visiting?
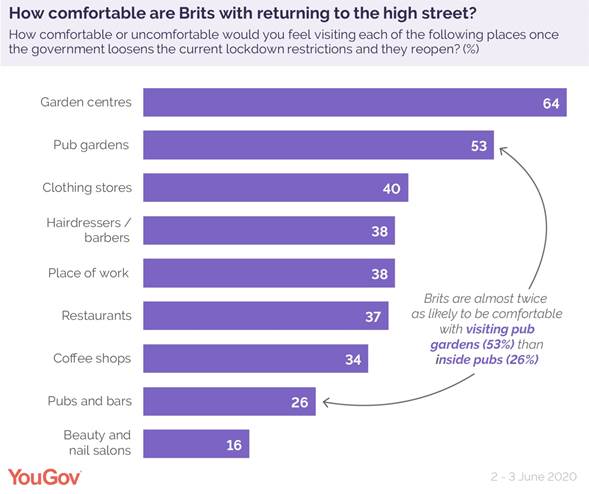
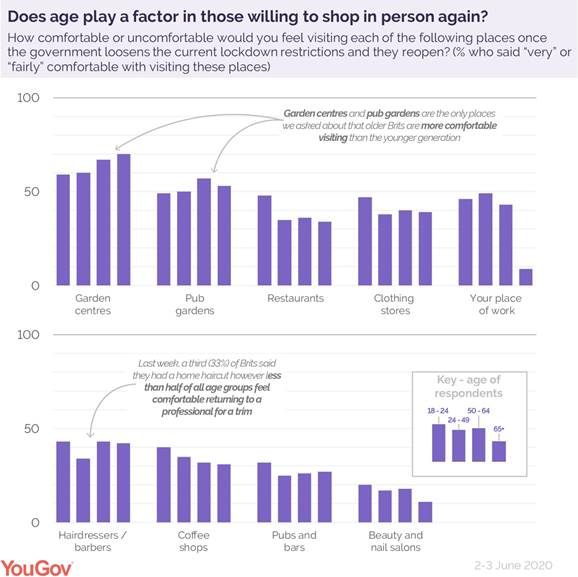
Of the high street shops opening today, clothing stores are the place Brits will feel most comfortable returning (40%). But this is some way off garden centres (64%) which opened on the 13th of May. These take the top spot as the place Brits are most comfortable returning to, possibly due to their open-aired nature.
Another two fifths (40%) of Brits say they would also be comfortable returning to indoor shopping centres and malls, with 9% very comfortable doing so – however half (50%) of Brits say they wouldn’t be comfortable heading into their local indoor shopping centre just yet.
Looking at other locations up and down the high street which haven’t opened just yet - approaching two fifths of Brits (37%) say they will feel comfortable returning to restaurants when they eventually reopen. Around the same (34%) say they are comfortable with returning to coffee shops, some of which have already begun to offer takeaway services. The 38% of Brits who feel comfortable enough to return to their barber or hairdresser will have to wait however, with these outlets remaining closed until the 4th of July.
We also asked Brits how they feel about returning to the gym. Considering 74% of Brits told YouGov they were exercising during lockdown, how many are heading to gyms when they reopen? Around a quarter (27%) of regular gym goers say they feel comfortable returning.
In this an age issue?
In April, economic researchers from the University of Warwick made a case for ending lockdown for young adults, who are less at risk of developing serious cases of COVID-19 and could breathe life back into the economy – however our research shows that in many of the scenarios we asked about, the difference in comfort between age brackets is low, and in some cases older Brits are more willing to return than their younger peers.
The biggest difference between age groups (not including the workplace) is for restaurants, where 48% of Brits aged 18 to 24 feel comfortable visiting, compared to 38% of those aged over 65 - a 14 percentage point difference.
In the case of of garden centres and pub gardens, the larger, open-air nature of these places may explain why older Brits are more comfortable returning to these places than younger generations. These places are also where most Brits think they will be able to adhere to social distancing guidelines.
Are feelings of comfort in
returning to the high street tied to social distancing?
The majority of Brits think they can keep to rules when visiting garden centres (71%) and pub gardens (60%) however these are the only places where the majority think they can do so. Despite retail workers’ best efforts to prepare stores with plastic shielding, one-way systems and two-metre floor markers, just 48% of Brits think they will be able to keep two metres away from other shoppers in clothes shops.
What this data suggests is that how comfortable people feel returning to these locations is related to how well they think they will be able to socially distance from others while they are there. For example, Brits are twice as likely to feel comfortable returning to pub gardens (53%) than indoor pubs (26%), and are also twice as likely to think they could socially distance in a pub garden (60%) than inside a pub or bar (29%).
Interestingly, the perceived ability to socially distance does not follow the same age-related pattern as we saw in comfortability to visit places – for example 37% of over 65s think they could socially distance at the hairdressers, compared to 29% of 18- to 24-year-old Britons. However, this younger age bracket are then more likely to think they can socially distance in coffee shops (51%) compared to the over 65s (39%).
Could shops take precautions
other than the two metre rule?
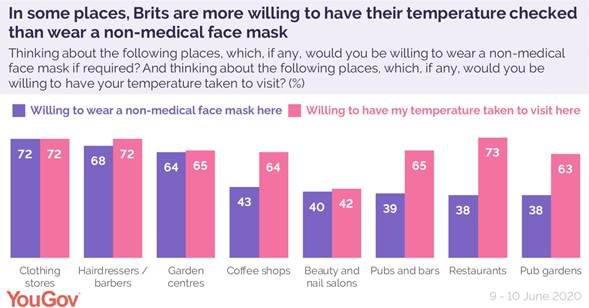
Following on from this, what other precautions are Britons willing to take to return to the high street? We asked whether Britons would be willing to wear a face mask if required (something Britons have been historically opposed to doing voluntarily), and if they would be willing to have their temperature taken before visiting places.
Interestingly, Britons are most willing to take these extra precautions in the places where they say they are least confident at maintaining the two metre social distancing rule. Approaching three quarters (72%) of Brits say they would be willing to both wear and mask and have a temperature check before shopping in clothes shops, and similar numbers say the same (68% and 72%) for barbers and hairdressers.
YouGov recently reported that a mere 21% of Brits were donning face masks when they left the house, which makes it unsurprising that in some scenarios (pub gardens, restaurants, and pubs and bars) Brits are more willing to have a temperature check than wear a mask. The biggest disparity is in the restaurant scenario, where Brits are almost twice as likely to be willing to submit to a temperature check (73%) than wear a non-medical facemask (38%).
Simply, is it too soon for us
to be out shopping?
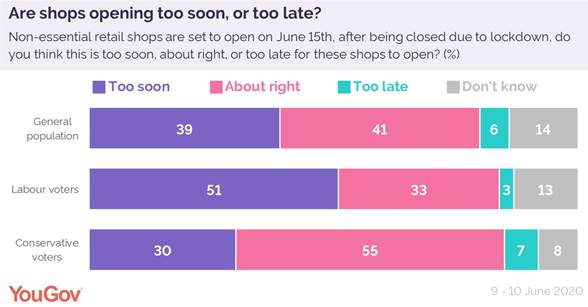
This all begs the simple question: is it too soon for non-essential shops to open their doors? The public as a whole is split, with 39% saying it is, and 41% believing it’s about the right time for shops to open. Just 6% of the public think non-essential retail shops should have already reopened.
There is a significant difference between Labour and Conservative voters on the issue, with Conservative voters more likely to back the Government, with 55% saying it’s the right time, and three in ten (30%) who think it’s too soon. This is compared to half (51%) of Labour voters who say it’s too soon, and 33% who are pleased to see the shops reopen.
(YouGov)
June 14, 2020
642-43-11/Poll
Over a fifth of key workers lose income if they self-isolate
About a fifth of essential workers have had to isolate during the coronavirus outbreak – this puts many in a financially precarious situation
New YouGov data shows that 22% of key workers face some reduction in their income if they self-isolate. This includes 6% who don’t get paid at all, while 11% receive statutory sick pay (£95.85 per week). Additionally, 5% receive more than statutory sick pay but less than their normal salary.
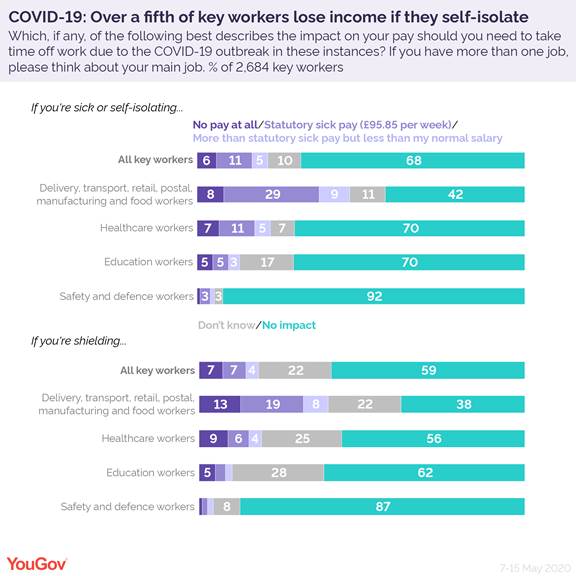
Close to a fifth (18%) of critical workers also miss out on pay if they have to shield due to being in a high-risk group, including 7% who receive no income at all. The actual numbers could be higher as over a fifth (22%) are uncertain.
Workers in the lowest paid sectors least likely to get paid if ill or shielding
Nearly half of essential workers in sectors like delivery, transport and food (47%) report that they would miss out on income if they were to self-isolate. In this group, 8% of workers would receive no pay at all, while 29% would have to get by on £95.85 per week.
Similarly, two in five workers in these sectors say their pay would be impacted if they needed to shield due to being in a high-risk group. This includes 13% who would not get paid at all, while 19% would have to live off statutory sick pay.
These workers include the people who deliver your parcels, takeaway orders and keep the public transport network running. They are the lowest paid among all essential staff. Over two in five (43%) earn under £25,000 a year, compared with an average of 26% across all key workers.
Among healthcare staff, who are the most exposed to the virus, nearly a quarter would lose some (16%) or all of their income (7%) if self-isolating. Nearly a fifth would also take a financial hit if they had to shield, including 9% who would not get paid at all.
Teachers and other education worker are in a slightly better position, although 13% would lose income if self-isolating. One in ten would also see some reduction in their earnings if shielding.
Prison guards, police officers and other safety and defence workers are mostly guaranteed income, with much lower numbers saying their pay would be affected if self-isolating (5%) or shielding (4%).
About a fifth of critical workers have had to self-isolate during outbreak
Among all key workers, 19% have had to isolate during the coronavirus outbreak. The figure includes 12% who displayed symptoms, while 7% did not but had been in contact with someone with suspected or confirmed coronavirus. A further 1% said they experienced symptoms but did not isolate.

Healthcare workers are most exposed to the virus with 23% having isolated at some point – the highest of any group. Among these, 16% experienced symptoms, while 7% were asymptomatic.
Among teachers and education staff, 18% have had to quarantine. The figure is similar for safety and defence staff such as police officers and prison guards (17%).
Workers in sectors that include delivery, transport, retail, postal, manufacturing and food appear slightly less exposed, however 11% have still had to self-isolate. A further 2% say they’ve experienced symptoms but did not isolate.
The figures also vary between regions. London has the highest number of key workers who have quarantined themselves (22%) while Wales and Scotland, both at 16%, have the lowest.
(YouGov)
June 11, 2020
NORTH AMERICA
642-43-12/Poll
Canada's support for Israel in the spotlight ahead of key UN vote
As Canada vies for UNSC seat, new survey shows 74 percent of its citizens want country to oppose Israel annexation plan.
Most Canadians want Prime Minister Justin Trudeau's government to oppose Israel's illegal plans to annex parts of the occupied West Bank, according to a new poll released ahead of a vote on Canada's bid for a seat on the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
The poll, conducted by EKOS Research Associates and published on Tuesday, showed that three out of four Canadians want their government to express opposition to Israeli annexation in some form, while 42 percent supported the use of economic or diplomatic sanctions against Israel.
The survey's authors said it "confirms that Canadian foreign policy is out of touch with the preferences of Canadians" as Ottawa competes for a non-permanent seat at the UNSC.
Canada is facing off against Norway and Ireland in Wednesday's vote, where the three nations are vying for two seats.
To win the coveted position, Canada will have to obtain two-thirds of the vote in the UN General Assembly (UNGA) - or 128 votes if all 193 nations vote. Trudeau's government has invested heavily in the effort, but rights groups have opposed the bid, noting Canada's staunch support of Israel.
Thomas Woodley, president of Canadians for Peace and Justice in the Middle East which cosponsored the survey, said its "results prove that Canadians want more than words from Trudeau when it comes to opposing Israel's annexation".
"Not only is it necessary to threaten sanctions to discourage annexation from taking place, but there is considerable support among the Canadian public to do so," he said in a statement.
![Infographic Palestine loss of land map [DO NOT USE]](642_files/image047.jpg)
Israel's plan to annex a third of the occupied West Bank featured heavily in a proposed "Middle East plan" announced by US President Donald Trump in January. Trump's "plan" suggested a Palestinian state reduced to isolated enclaves with no control over its borders.
The "plan" prompted widespread criticism, with more than 50 European former foreign ministers and leaders saying it "has characteristics similar to apartheid".
But Canada remained largely silent on the issue.
On June 1, more than 100 organisations and dozens of prominent figures delivered an open letter to all UN ambassadors, urging countries to vote for Ireland and Norway instead of Canada.
The letter pointed out that Trudeau's government has voted against more than 50 UNGA resolutions upholding Palestinian rights that were backed by the majority of member states. In total, Canada has voted against 166 resolutions critical of Israel's treatment of Palestinians since 2000 - when Ottawa last held a seat on the UNSC.
The letter also noted Canada's refusal to abide by UNSC Resolution 2334, which was passed in 2016 and called on member states to "distinguish, in their relevant dealings, between the territory of the State of Israel and the territories occupied in 1967". Instead, Canada "extends economic and trade assistance to Israel's illegal settlement enterprise", the letter said, also slamming the former Canadian foreign minister's remark that Ottawa would act as an "asset for Israel" should it win a seat on the UNSC.
The mounting criticism forced Trudeau earlier this month to clarify his position on Israel's annexation plan.
"I have highlighted both publicly and directly to Prime Minister Netanyahu and alternate Prime Minister Benny Gantz the importance of staying away from measures that are unilateral and our deep concerns and disagreement with their proposed policy of annexation," Trudeau said at the June 2 news briefing.
It was the first time Trudeau mentioned the annexation plan since January.
Marc-Andre Blanchard, Canadian ambassador to the UN, also hit back at the rights groups' allegations, saying their open letter contained "significant inaccuracies" and mischaracterised Canada's position on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
In his own letter (PDF) to all UN ambassadors on June 10, Blanchard said Canada supported the creation of a Palestinian state, "living side-by-side in peace and security with Israel".
The only means to a two-state solution is direct negotiations, he said, adding: "Canada views any unilateral annexation of parts of the West Bank as contrary to international law. Canada has expressed deep concern and disagreement with the proposed policy of annexation and raised the issue publicly."
But critics say it was too little, too late.
"The question is: Then what?" asked Corey Balsam at the Independent Jewish Voices, highlighting the need for action against Israel to ensure accountability.
"Trudeau speaks a lot about the importance of maintaining a rules-based international order ... but of course, annexation is at complete odds with international law and those rules," Balsam said.
"Canada's staunch support for Israel has been one reason why they haven't gotten a UNSC seat in the past. We'll see [on Wednesday] if they are successful this time."
|
What is in Trump's Middle East plan? |
Michael Lynk, UN special rapporteur for the situation of human rights in the occupied Palestinian territories, also questioned Canada's silence on Israeli annexation plans, given its opposition to Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014.
In March, Canada issued a statement to mark the sixth anniversary of Russia's annexation of Crimea in which its opposition to annexation was clear: "Canada unequivocally condemns this violation of Ukraine's sovereignty and territorial integrity and of international law."
But on the Palestinian issue, "Canada has had a bad case of diplomatic laryngitis," Lynk said. "Canada puts itself in a weak position as it campaigns for a UN security seat."
He added: "It would be interesting to see how Canada makes out in its current Security Council bid against Ireland and Norway who have a principled position in respect to international law and its application to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict."
(Al Jazeera)
June 17, 2020
Source: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/06/canada-support-israel-spotlight-key-vote-200616183626119.html
642-43-13/Poll
Americans’ views on World Health Organization split along partisan lines as Trump calls for U.S. to withdraw
The World Health Organization, a specialized agency of the United Nations, has historically served several public health functions, including fighting communicable and non-communicable diseases. It has played a high-profile role in addressing the global spread of the coronavirus, which it characterized as a pandemic in early March. But in mid-April, U.S. President Donald Trump ordered his administration to halt U.S. funding of the organization, accusing it of making a series of consequential mistakes in its handling of COVID-19. On May 29, Trump announced that he would seek to terminate the country’s relationship with the WHO completely and redirect funds toward other world public health needs.
Amid scrutiny of the WHO, here are key facts about the organization and how Americans see it.
1The WHO is funded by the UN, other intergovernmental organizations and a slew of nongovernmental organizations and private donors. Funding is made up of both required (or “assessed”) contributions from member states and voluntary contributions, which can also come from member states. In 2018, roughly half (51%) of the organization’s total funding came from its 194 member states’ assessed and voluntary contributions.
The total approved WHO budget for the 2020-2021 fiscal biennium is roughly $4.8 billion.
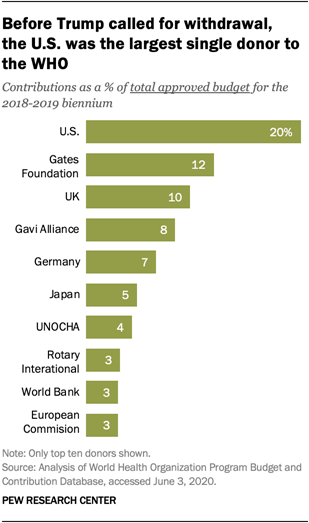 2The United States was the largest contributor to the
WHO in the 2018-2019 biennium, giving just over $893 million, or about 20% of
its approved budget that cycle. The second largest donor was
the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which contributed roughly 12%. Other top
donors include Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance; the UN Office for the Coordination
of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA); Rotary International; the World Bank; the
European Commission; and other WHO member states including the UK, Germany and
Japan.
2The United States was the largest contributor to the
WHO in the 2018-2019 biennium, giving just over $893 million, or about 20% of
its approved budget that cycle. The second largest donor was
the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which contributed roughly 12%. Other top
donors include Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance; the UN Office for the Coordination
of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA); Rotary International; the World Bank; the
European Commission; and other WHO member states including the UK, Germany and
Japan.
It is not clear whether Trump has unilateral authority to cut U.S. funding to the organization. Since 2010, at least 10 different federal agencies have sent money to the WHO. Prior to Trump’s decision, the U.S. was expected to make contributions equal to roughly 11% of the WHO’s 2020-2021 budget. (More information on U.S. funding of international organizations is available from the State Department.)
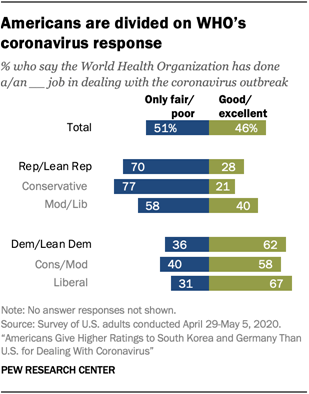 3Just 46% of Americans give the WHO positive marks on its coronavirus response, though views of how
well the organization has dealt with the outbreak are sharply divided along
partisan lines. Whereas 62% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning
independents say the organization has done at least a good job in handling the
pandemic, only 28% of Republicans and GOP leaners say the same.
3Just 46% of Americans give the WHO positive marks on its coronavirus response, though views of how
well the organization has dealt with the outbreak are sharply divided along
partisan lines. Whereas 62% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning
independents say the organization has done at least a good job in handling the
pandemic, only 28% of Republicans and GOP leaners say the same.
The public rates the WHO’s pandemic response more negatively than that of national health authorities. When last polled in late April and early May, 72% of U.S. adults said public health officials such as those at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were doing at least a good job, with a much smaller partisan gap in opinion (only 7 percentage points).
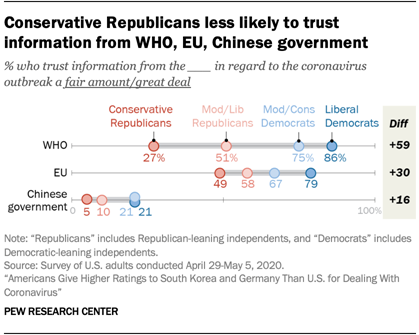 4Overall, 59% of Americans trust information from the WHO regarding
the coronavirus outbreak. Trust is highest
among younger adults and those with more education, though differences by
education and age are relatively small compared with those by partisan
identification and ideology. For example, 86% of liberal Democrats and
Democratic-leaning independents say they trust information from the WHO at
least a fair amount, compared with 27% of conservative Republicans and GOP
leaners.
4Overall, 59% of Americans trust information from the WHO regarding
the coronavirus outbreak. Trust is highest
among younger adults and those with more education, though differences by
education and age are relatively small compared with those by partisan
identification and ideology. For example, 86% of liberal Democrats and
Democratic-leaning independents say they trust information from the WHO at
least a fair amount, compared with 27% of conservative Republicans and GOP
leaners.
Partisans are somewhat less divided when it comes to trusting information about the coronavirus outbreak from the European Union, which is generally trusted, and the Chinese government, which is broadly distrusted.
In his criticisms of the WHO, Trump has argued that the organization has been too trusting of coronavirus-related information from the Chinese government.
(Pew Research Center)
June 11, 2020
642-43-14/Poll
Unemployment rose higher in three months of COVID-19 than it did in two years of the Great Recession
The COVID-19 outbreak and the economic downturn it engendered swelled the ranks of unemployed Americans by more than 14 million, from 6.2 million in February to 20.5 million in May 2020. As a result, the U.S. unemployment rate shot up from 3.8% in February – among the lowest on record in the post-World War II era – to 13.0% in May. That rate was the era’s second highest, trailing only the level reached in April (14.4%).
The rise in the number of unemployed workers due to COVID-19 is substantially greater than the increase due to the Great Recession, when the number unemployed increased by 8.8 million from the end of 2007 to the beginning of 2010. The Great Recession, which officially lasted from December 2007 to June 2009, pushed the unemployment rate to a peak of 10.6% in January 2010, considerably less than the rate currently, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of government data.
How we did this
The unemployment rate in May might have been as high as 16%, by the U.S. government’s estimate. But it is not recorded as such because of measurement challenges that have arisen amid the coronavirus outbreak. Also, a sharp decline in labor force participation among U.S. workers overall may be adding to the understatement of unemployment. In May, 9 million Americans not in the labor force were in want of a job compared with 5 million in February, per government estimates. But these workers are not included in the official measure of unemployment. Thus, the COVID-19 recession is comparable more to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the unemployment rate is estimated to have reached 25%.
Unemployment among all groups of workers increased sharply in the COVID-19 recession. But the experiences of several groups of workers, such as women and black men, in the COVID-19 outbreak vary notably from how they experienced the Great Recession. Here are five facts about how the COVID-19 downturn is affecting unemployment among American workers.
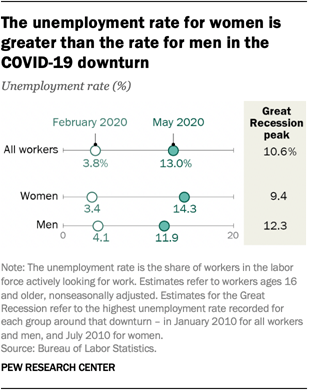 1The unemployment rate for women in May (14.3%) was
higher than the unemployment rate for men (11.9%). This stands
in contrast to the Great Recession, when the unemployment rate for women had
peaked at 9.4% in July 2010 compared with a peak of 12.3% for men in January
2010.
1The unemployment rate for women in May (14.3%) was
higher than the unemployment rate for men (11.9%). This stands
in contrast to the Great Recession, when the unemployment rate for women had
peaked at 9.4% in July 2010 compared with a peak of 12.3% for men in January
2010.
One reason women have seen a greater rise in unemployment in the current downturn is that they accounted for the majority of workers on the payrolls of businesses in the leisure and hospitality sector and educational services sector in February. Employment in these two sectors fell by 39% and 15% from February to May, respectively, leading most other sectors by a wide margin. By contrast, job losses in the Great Recession arose primarily from the construction and manufacturing sectors, where women have a much lighter footprint than men.
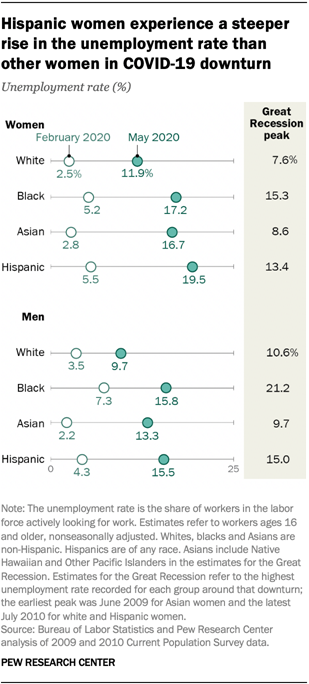 2The unemployment rate for black men in May (15.8%)
was substantially less than
the peak rate they faced in the Great Recession (21.2%). Black
men are the only group among those examined in this analysis for whom such a
notable gap exists. The reasons for this are not entirely clear but are
likely rooted in the occupation and industry distributions of black men.
Recessions in which the turmoil is centered in goods-producing sectors, such as
the Great Recession, appear to take a greater toll on the job prospects of
black men. The unemployment rate for black men previously topped 20% in
the twin recessions of the early 1980s, when manufacturing employment
also took a
sharp dive.
2The unemployment rate for black men in May (15.8%)
was substantially less than
the peak rate they faced in the Great Recession (21.2%). Black
men are the only group among those examined in this analysis for whom such a
notable gap exists. The reasons for this are not entirely clear but are
likely rooted in the occupation and industry distributions of black men.
Recessions in which the turmoil is centered in goods-producing sectors, such as
the Great Recession, appear to take a greater toll on the job prospects of
black men. The unemployment rate for black men previously topped 20% in
the twin recessions of the early 1980s, when manufacturing employment
also took a
sharp dive.
Among other men, Hispanic workers faced an unemployment rate of 15.5% in May, higher than the rates for Asian (13.3%) and white (9.7%) men. While the unemployment rates for Asian and white men increased sharply in the COVID-19 recession, they remain below the rates for black and Hispanic men.
Hispanic women had the highest rate of unemployment in May (19.5%), compared with other women or men among the nation’s major racial and ethnic groups. The unemployment rate among white women jumped nearly fivefold, climbing from 2.5% in February to 11.9% in May. A steep increase in the unemployment rate among Asian women also pushed their unemployment rate in May (16.7%) to near parity with the unemployment rate among black women (17.2%). The recent experience of white and Asian women stands in contrast to their experience in the Great Recession, when their unemployment rates peaked at levels substantially below the levels reached for black and Hispanic women.
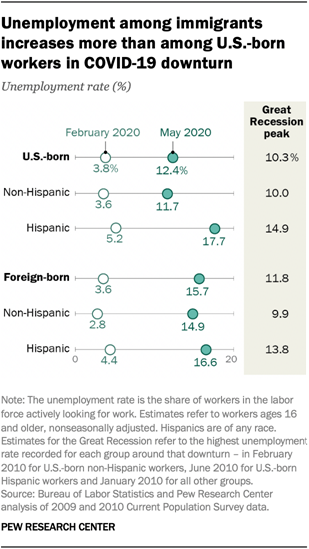 3Immigrants saw their unemployment rate jump higher
than the rate for U.S.-born workers in the COVID-19 downturn, mirroring
their experience in the Great Recession. In February, immigrants and U.S.-born
workers had similarly low rates of unemployment, 3.6% and 3.8%, respectively.
By May, the unemployment rate for immigrants had risen to 15.7%, compared with
12.4% for U.S.-born workers.
3Immigrants saw their unemployment rate jump higher
than the rate for U.S.-born workers in the COVID-19 downturn, mirroring
their experience in the Great Recession. In February, immigrants and U.S.-born
workers had similarly low rates of unemployment, 3.6% and 3.8%, respectively.
By May, the unemployment rate for immigrants had risen to 15.7%, compared with
12.4% for U.S.-born workers.
The steeper increase in the unemployment rate for immigrants is driven by the experience of Hispanic workers who comprised 47% of the immigrant workforce in February, compared with 12% of the U.S.-born workforce. Compared with non-Hispanic workers, Hispanic workers are relatively young and are less likely to have graduated from college. Additionally, 44% of Hispanic immigrants in the labor force are estimated to have been unauthorized in 2016. These characteristics of Hispanic workers make them more vulnerable to job losses in economic downturns.
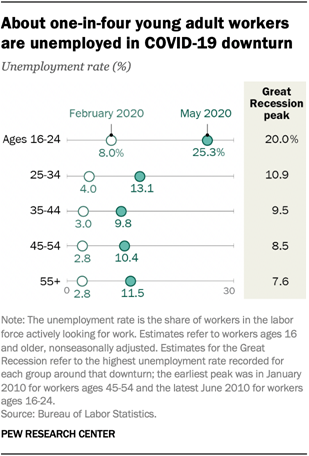 4Workers in all but one age group saw their
unemployment rate climb into the double digits in May due to the COVID-19
outbreak, unlike the Great Recession when this was true only
for younger workers. The unemployment rate among young adults ages 16 to 24
(25.3%) exceeded the rate among other workers by a substantial margin in May,
more than double the rate among workers 35 and older. A key reason is the
concentration of young adults in higher-risk
industries, such as food services and drinking places, that were more
affected by the need for social distancing and government mandated shutdowns.
4Workers in all but one age group saw their
unemployment rate climb into the double digits in May due to the COVID-19
outbreak, unlike the Great Recession when this was true only
for younger workers. The unemployment rate among young adults ages 16 to 24
(25.3%) exceeded the rate among other workers by a substantial margin in May,
more than double the rate among workers 35 and older. A key reason is the
concentration of young adults in higher-risk
industries, such as food services and drinking places, that were more
affected by the need for social distancing and government mandated shutdowns.
Changes in the unemployment rate by age in the COVID-19 recession are consistent with patterns in past recessions. During the Great Recession the unemployment rate for young adults peaked at 20% in June 2010, compared with no greater than 10.9% among older workers.
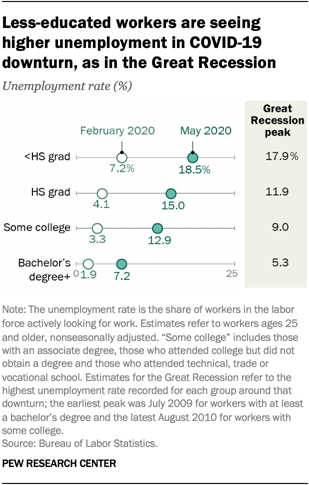 5Unemployment rates in the COVID-19 downturn are lower
among workers with higher levels of education, as in the Great
Recession. The unemployment rate in May was lowest among workers with a
bachelor’s degree or higher education (7.2%), the only group among those
examined not to experience an unemployment rate in the double digits. In
contrast, 18.5% of workers without a high school diploma were unemployed in May.
In the Great Recession, the peak unemployment rates for the different groups
ranged from 5.3% among those with a bachelor’s degree or higher education to
17.9% among those without a high school diploma.
5Unemployment rates in the COVID-19 downturn are lower
among workers with higher levels of education, as in the Great
Recession. The unemployment rate in May was lowest among workers with a
bachelor’s degree or higher education (7.2%), the only group among those
examined not to experience an unemployment rate in the double digits. In
contrast, 18.5% of workers without a high school diploma were unemployed in May.
In the Great Recession, the peak unemployment rates for the different groups
ranged from 5.3% among those with a bachelor’s degree or higher education to
17.9% among those without a high school diploma.
A unique factor in the COVID-19 recession is the significance of teleworking in keeping people on the job. The option to telework varied considerably across workers in February depending on their education level, with those with a college degree six times as likely to have the option as those without a high school diploma, 62% vs. 9%. Nonetheless, the May unemployment rate among college graduates was nearly four times that of February.
(Pew Research Center)
June 11, 2020
642-43-15/Poll
#BlackLivesMatter surges on Twitter after George Floyd’s death
As nationwide protests continue over police brutality and the death of George Floyd, the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag, which is often used in connection with police-related deaths of black Americans, has been used roughly 47.8 million times on Twitter – an average of just under 3.7 million times per day – from May 26 to June 7, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of publicly available tweets.
Public reactions to the death of Floyd – an unarmed black man – on May 25 while in the custody of Minneapolis police emerged quickly on Twitter. There were roughly 218,000 tweets containing the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag the day after his death, when the first bystander video was posted online. Once protests began in Minneapolis and spread across the country and around the world, daily use of the hashtag passed 1 million on May 27.
On May 28, nearly 8.8 million tweets contained the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag – making this the highest number of uses for this hashtag in a single day since the Center started tracking its use. After that peak, the number of tweets containing the hashtag consistently remained above 2 million uses per day through Sunday, June 7. This is the highest volume of sustained mentions of #BlackLivesMatter in tweets over the time period the Center has studied.
How we did this
This new analysis also highlights how use of the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag often increases around major news events related to race, violence and criminal justice. For instance, in early May, the hashtag spiked following the release of a video capturing the shooting death of black jogger Ahmaud Arbery by white men in Georgia that occurred in February 2020. There were nearly 86,000 posts containing the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag on May 7, two days after the video emerged.
The phrase “black lives matter” first gained attention after it was used by a black community organizer in a Facebook post following the 2013 acquittal of George Zimmerman in the shooting death of black teenager Trayvon Martin in Florida. Previous Center analyses of the hashtag show that its use and its influence grew to national prominence after Ferguson, Missouri, police officer Darren Wilson fatally shot Michael Brown in 2014 but was not indicted in the death of the black teen in November of that year.
There have been a number of increases in the daily use of the hashtag since Ferguson. One of the most notable spikes occurred over a period of roughly 10 days in in the summer of 2016, when the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag was mentioned an average of nearly 500,000 tweets daily. This time span included news of Alton Sterling being fatally shot by police officers in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, on July 5, 2016. The following day, Philando Castile was shot and killed by a police officer in the suburbs of St. Paul, Minnesota. Then, on July 7, during protests of these deaths, a black gunman killed five police officers in Dallas. Another black shooter killed three officers in Baton Rouge roughly a week and half later.
At the time, these 10 days accounted for the largest numbers of mentions of the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag, according to a 2018 Center report.
Pew Research Center’s previous analysis of the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag covered the period from Jan. 1, 2013, to May 1, 2018, while the most recent analysis studies the period from May 1, 2018, through June 7, 2020. The more recent data collection phase was used for May 1, 2018, in this analysis. Both employed automated coding software developed by Crimson Hexagon, a firm now part of Brandwatch. It is important to note that these searches were performed at different points in time. There may be methodological or other differences in the software used then and now that make these studies not exactly comparable. However, the overall trend is the same and highlights that the #BlackLivesMatter hashtag continues to have periodic increases in daily use, often times in response to news and discussion related to fatal encounters between law enforcement and black Americans.
(Pew Research Center)
June 10, 2020
642-43-16/Poll
A majority of Americans say immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want
Americans generally agree that immigrants – whether undocumented or living legally in the country – mostly do not work in jobs that U.S. citizens want, with a majority saying so across racial and ethnic groups and among both political parties. This is particularly true when it comes to undocumented immigrants. About three-quarters of adults (77%) say undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want, while 21% say undocumented immigrants fill jobs U.S. citizens would like to have, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted April 29 to May 5.
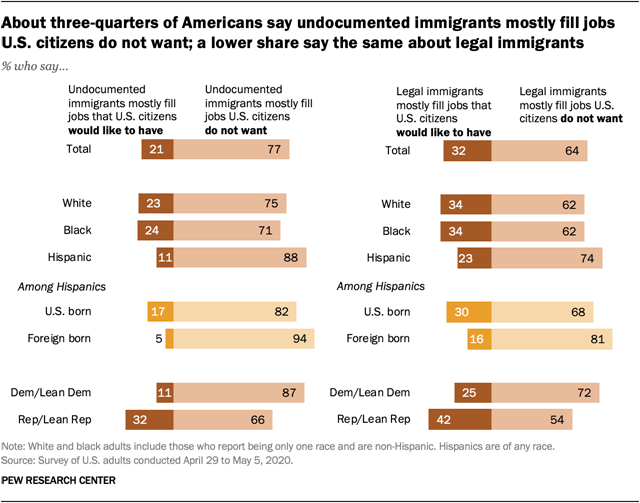 Hispanics
(88%) are most likely to say undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S.
citizens do not want, with more Hispanic immigrants than U.S.-born Hispanics
saying so (94% vs. 82%). By comparison, similar shares of white (75%) and black
(71%) adults say the same.
Hispanics
(88%) are most likely to say undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S.
citizens do not want, with more Hispanic immigrants than U.S.-born Hispanics
saying so (94% vs. 82%). By comparison, similar shares of white (75%) and black
(71%) adults say the same.
The findings are little changed from August 2019, when 77% of U.S. adults said undocumented immigrants fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want. They come amid mounting job losses across the nation during the COVID-19 outbreak. The U.S. unemployment rate soared to 14.7% in April, up from 4.4% in March, the highest monthly rate since 1948. In May, it was 13.3%. The Center’s April-May survey found most Americans say the federal government does not have a responsibility to provide economic help to undocumented immigrants who have lost their job due to the outbreak.
How we did this
Some of the biggest differences in views of whether undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want are along party lines. The vast majority of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (87%) say this, compared with 66% of Republicans and Republican leaners. However, partisan differences are significantly wider on other issues related to undocumented immigrants.
Differences also exist by educational attainment. Large shares of U.S. adults with a postgraduate degree (88%) and those with a bachelor’s degree (84%) say undocumented immigrants mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want, compared with 78% of those with some college experience and 69% of those with a high school diploma or less.
A majority of Americans across various groups also say legal immigrants currently in the country mostly fill jobs U.S. citizens do not want. Nearly two-thirds (64%) of Americans say this, including similar shares of white and black adults (62% each). About three-quarters of Hispanics (74%) say the same, with a higher share of Hispanic immigrants (81%) than U.S.-born Hispanics (68%) saying so. About 70% of the nation’s 42 million Hispanic adults have close immigrant connections – roughly 19 million are immigrants themselves, and almost 10 million born in the United States have at least one parent who is an immigrant, according to estimates from 2019 and 2020 Current Population Survey data.
Many immigrants living legally in the U.S. hold jobs deemed essential by the federal government, including an estimated 2.7 million who worked in the health care sector, or nearly 15% of all health care workers as of 2017, the most recent year for which Center estimates on both legal and unauthorized immigrant populations are available.
Unauthorized immigrant
workers in the U.S.
 An estimated
7.6 million undocumented (or unauthorized) immigrants worked in the U.S. as of
2017 – down from a peak of 8.3 million in 2008 – accounting for nearly 5% of
all U.S. workers.
An estimated
7.6 million undocumented (or unauthorized) immigrants worked in the U.S. as of
2017 – down from a peak of 8.3 million in 2008 – accounting for nearly 5% of
all U.S. workers.
About 750,000 unauthorized immigrants held jobs in industries that produce and distribute food – food production (290,000), food processing (210,000), food retail (170,000) and food distribution (70,000). During the COVID-19 outbreak, these industries, considered part of the nation’s food supply chain, are considered essential jobs. Unauthorized immigrants in these four industry groups accounted for more than 9% of workers in these food sectors in 2017, nearly double their share among all U.S. workers. Together, legal and unauthorized immigrants made up nearly a quarter (23%) of the nation’s nearly 8.2 million workers in food industries.
Many undocumented immigrants work in industries that are at risk for job loss during the current coronavirus outbreak because they hold positions that are difficult to perform remotely. In all, 84% of undocumented immigrant workers held such jobs in 2017, including those in the service sector (2.3 million workers) and construction sector (1.3 million workers). By comparison, 62% of U.S. workers held these types of jobs. Much of the difference between these groups is due to undocumented immigrants’ jobs being more difficult to telework, even if the job is in an industry, like education and health, where large shares can work remotely.
The Trump administration has largely halted legal immigration to the U.S. in recent months, though it has temporarily changed visa rules for foreign guest workers to make it easier for them to remain employed at meat processing plants and other food and agriculture jobs. Although unauthorized immigration has slowed in recent years, this spring’s steep drop in apprehensions at the U.S.-Mexico border could be a sign that unauthorized immigration into the U.S. has slowed further during the outbreak.
Detailed tables: Legal and
unauthorized immigrant workers by state
California had about 6.7 million immigrant workers as of 2017, the most in the nation, which account for nearly a quarter of all U.S. immigrant workers. The state had 5.2 million legal immigrant workers (24% of all U.S. legal immigrant workers) and 1.5 million unauthorized immigrant workers (20% of all U.S. unauthorized immigrant workers). Texas had the next largest immigrant workforce, with 2.1 million legal immigrant workers and 1.1 million unauthorized immigrant workers.
In California, about 570,000 immigrants held jobs in food production and distribution industries that make up the nation’s food chain, the most in the nation as of 2017. They account for about half of the state’s workers in these industries – 33% are legal immigrants and 17% are unauthorized immigrants. In Texas, 170,000 immigrants work in food industries, the next highest total. They are 28% of the state’s food workers – 17% are legal immigrants and 11% are unauthorized immigrants.
Industries and occupations
of U.S. legal and unauthorized immigrants
 Unauthorized
immigrants accounted for nearly 5% of the U.S. workforce in 2017, while legal
immigrants accounted for nearly 13% of workers.
Unauthorized
immigrants accounted for nearly 5% of the U.S. workforce in 2017, while legal
immigrants accounted for nearly 13% of workers.
Among industries, which refer to the kind of business conducted by an employer, immigrants accounted for more than a quarter of workers in the agriculture sector, the highest of any industry. Unauthorized immigrants (14%) and legal immigrants (15%) accounted for similar shares of agriculture workers.
Compared with their share of the U.S. workforce, a relatively high share of unauthorized immigrants also worked in industries such as construction (12%), leisure and hospitality (8%), personal and other services (7%) and manufacturing (6%). While the share of U.S. legal immigrants in construction (13%) was similar to the unauthorized share, legal immigrants made up a higher share of workers in personal and other services (15%), manufacturing (14%) and leisure and hospitality (12%).
Detailed tables: Industry
and occupation groups
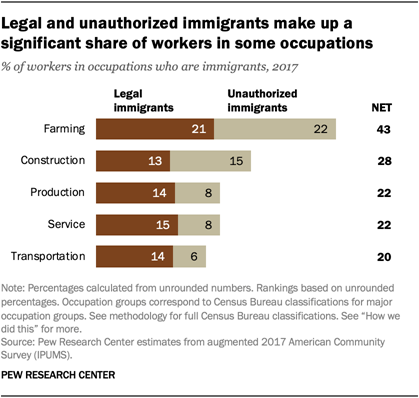 Among
occupations, which refer to the kind of work people do on the job, immigrants
have the largest presence in farming, where unauthorized (22%) and legal
immigrants (21%) accounted for more than four-in-ten workers as of 2017. In
construction jobs, unauthorized immigrants were 15% of all workers, more than
three times their share among all U.S. workers. By contrast, legal immigrants
accounted for 13% of workers in construction, similar to their share among
workers overall.
Among
occupations, which refer to the kind of work people do on the job, immigrants
have the largest presence in farming, where unauthorized (22%) and legal
immigrants (21%) accounted for more than four-in-ten workers as of 2017. In
construction jobs, unauthorized immigrants were 15% of all workers, more than
three times their share among all U.S. workers. By contrast, legal immigrants
accounted for 13% of workers in construction, similar to their share among
workers overall.
Compared with their share of the overall U.S. workforce, unauthorized immigrants had a larger presence in production (8%), service (8%) and transportation and material moving (6%). Meanwhile, the share of legal immigrants in these occupations was similar to their share among the U.S. workforce overall.
(Pew Research Center)
June 10, 2020
642-43-17/Poll
Hispanic women, immigrants, young adults, those with less education hit hardest by COVID-19 job losses
The economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 outbreak has been unsparing in its impact on the U.S. labor market. The number of employed workers fell by 24.7 million from February to April 2020 as the outbreak shuttered many parts of the economy. With the easing of government-mandated closures in recent weeks, employment picked up by 4.1 million from April to May. But overall, job losses remain sizable, with employment decreasing by 20.6 million (or 13%) from February to May. The downturn has affected some Americans more than others, particularly Hispanic women, immigrants, young adults and those with less education.
The decrease in employment in the first three months of the COVID-19 recession is more than double the decrease effected by the Great Recession over two years. From the end of 2007 to the end of 2009, U.S. employment fell by 8.0 million, or 5%. In addition, the impact of the COVID-19 recession on several groups of workers varies notably from their experiences in the Great Recession, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of government data.
While many American workers are hopeful they will get their old jobs back, analysts are unsure of the depth of the recession and the shape of the recovery that may follow. Here are five facts about how the employment of American workers is being affected by the COVID-19 downturn.
How we did this
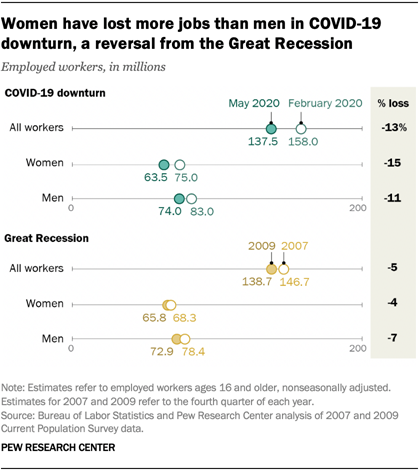 1More women than men lost their jobs from February to
May, 11.5 million vs. 9.0 million. In sharp contrast, men lost
more than twice as many jobs as women in the Great Recession from 2007 to 2009,
5.5 million vs. 2.5 million. Indeed, the COVID-19 downturn is the first of
eight downturns
in the past five decades in which women have lost more jobs than men.
1More women than men lost their jobs from February to
May, 11.5 million vs. 9.0 million. In sharp contrast, men lost
more than twice as many jobs as women in the Great Recession from 2007 to 2009,
5.5 million vs. 2.5 million. Indeed, the COVID-19 downturn is the first of
eight downturns
in the past five decades in which women have lost more jobs than men.
Rooted in the coronavirus outbreak, job losses in the latest recession have been concentrated in sectors in which social distancing of workers is difficult or the option to telework is lacking. Just three sectors – leisure and hospitality, education and health services, and retail trade – accounted for 59% of the total loss in nonfarm jobs from February to May. These sectors also accounted for 47% of jobs held by women in February, compared with 28% for men, exposing women to a higher risk of unemployment in recent months. Historically, job losses in recessions, including the Great Recession, have centered around goods-producing sectors, such as manufacturing and construction, in which men have a greater presence.
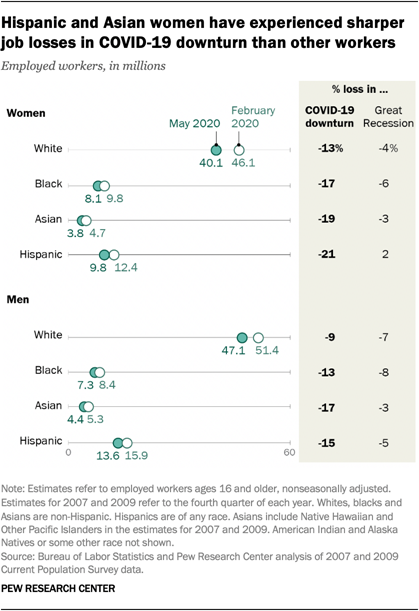 2Hispanic women have experienced a steeper decline in
employment (‑21%) in the COVID-19 downturn than other women or men. One
reason is that Hispanic women are more likely than others to be employed in
leisure and hospitality services; some 14% of Hispanic women were in 2018
compared with 10% of women and 8% of men overall. The leisure and hospitality
sector shed 39% of its workforce from February to May, far more than any other
sector. The employment of Hispanic women was essentially unchanged during
the Great Recession.
2Hispanic women have experienced a steeper decline in
employment (‑21%) in the COVID-19 downturn than other women or men. One
reason is that Hispanic women are more likely than others to be employed in
leisure and hospitality services; some 14% of Hispanic women were in 2018
compared with 10% of women and 8% of men overall. The leisure and hospitality
sector shed 39% of its workforce from February to May, far more than any other
sector. The employment of Hispanic women was essentially unchanged during
the Great Recession.
Among men, Asian (-17%), Hispanic (-15%) and black (-13%) workers have experienced a greater loss than white (-9%) workers in the COVID-19 recession. The pattern among men also contrasts with the Great Recession, when the rate of job loss among white and black workers was steeper than among Asian and Hispanic workers.
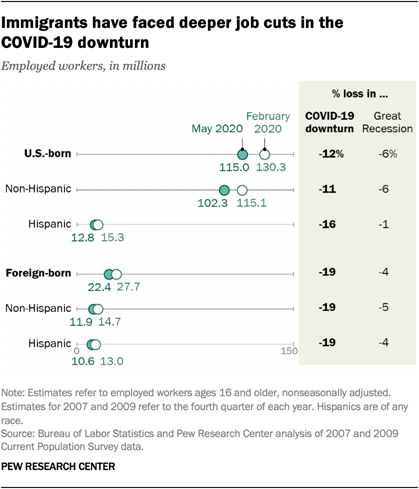 3Employment among immigrant workers has decreased more
sharply than among U.S.-born workers in the COVID-19 recession, a
19% drop compared with 12%. In the Great Recession, immigrants lost jobs at a
slightly slower pace than U.S.-born workers.
3Employment among immigrant workers has decreased more
sharply than among U.S.-born workers in the COVID-19 recession, a
19% drop compared with 12%. In the Great Recession, immigrants lost jobs at a
slightly slower pace than U.S.-born workers.
Among the U.S. born, Hispanic workers were more likely than non-Hispanic workers to have lost jobs from February to May. Among the foreign born, employment losses have been equally sharp for Hispanic and non-Hispanic workers, -19% for each group. Hispanics overall are relatively young and less likely to have graduated from college, two factors that put them at a higher risk of unemployment in economic downturns. Also, 44% of Hispanic immigrants in the workforce are estimated to have been unauthorized in 2016, which also likely made them more vulnerable to job cuts. The trends in employment among Hispanic workers are echoed in a Pew Research Center survey conducted April 29-May 5 in which Hispanic adults were more likely than American adults overall to say they have taken a pay cut or lost their job because of the coronavirus outbreak.
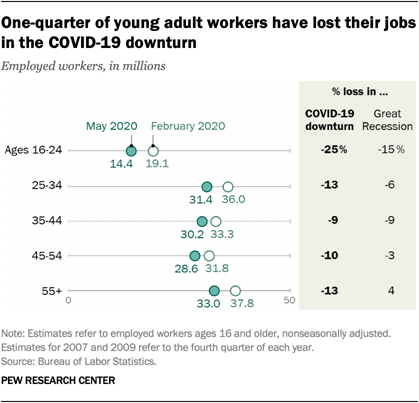 4The employment of young adult workers ages 16 to 24
has been severely impacted by the COVID-19 downturn, with
one-quarter of them losing their jobs from February to May. A key contributing
factor is that nearly half of young adult workers (48%) were employed in higher-risk
industries in February, compared with 24% of workers overall. Job
losses for older workers were also sizable, ranging from 9% to 13%, but less
severe than for young adults. The pattern of job losses by age in the COVID-19
recession is generally consistent with the pattern in the Great Recession
and in previous recessions.
In a Pew
Research Center survey conducted April 29-May 5 young adults ages 18
to 29 were also more likely than older Americans to say that they have lost a
job or taken a pay cut because of the coronavirus outbreak.
4The employment of young adult workers ages 16 to 24
has been severely impacted by the COVID-19 downturn, with
one-quarter of them losing their jobs from February to May. A key contributing
factor is that nearly half of young adult workers (48%) were employed in higher-risk
industries in February, compared with 24% of workers overall. Job
losses for older workers were also sizable, ranging from 9% to 13%, but less
severe than for young adults. The pattern of job losses by age in the COVID-19
recession is generally consistent with the pattern in the Great Recession
and in previous recessions.
In a Pew
Research Center survey conducted April 29-May 5 young adults ages 18
to 29 were also more likely than older Americans to say that they have lost a
job or taken a pay cut because of the coronavirus outbreak.
Notably, 4.8 million adults ages 55 and older, nearing the traditional retirement age, have lost their jobs in recent months. The experience of workers 55 and older in the COVID-19 recession is the opposite of their experience during the Great Recession, when their employment increased 4% from 2007 to 2009. One factor in the increase in employment among older workers in the Great Recession was their rising labor force participation prior to the recession, from 30% in 1995 to 40% in 2009, adding to their numbers in the workforce even amid a recession.
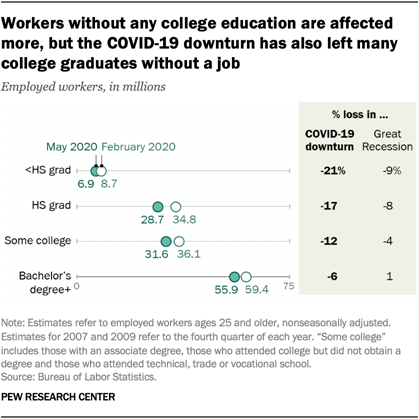 5Workers without any college education were more
likely to have lost their jobs than workers with at least some college
education in the COVID-19 downturn. The decrease in employment
from February to May ranged from 6% among workers with a college degree or more
education to 21% among workers without a high school diploma. This pattern in
job losses by education level is also in line with trends in recessions historically,
including the Great Recession.
5Workers without any college education were more
likely to have lost their jobs than workers with at least some college
education in the COVID-19 downturn. The decrease in employment
from February to May ranged from 6% among workers with a college degree or more
education to 21% among workers without a high school diploma. This pattern in
job losses by education level is also in line with trends in recessions historically,
including the Great Recession.
One difference between the COVID-19 recession and past recessions is in the significance of teleworking in saving jobs at the moment. Workers with a college degree or higher education are much more likely to have the option to telework – 62% could in February compared with 22% of high school graduates who did not go to college, for example. While this helped limit job losses for college graduates from February to May, their experience in the Great Recession was different – their employment was virtually unchanged from 2007 to 2009.
(Pew Research Center)
June 09, 2020
642-43-18/Poll
Amid Slow Return to Workplaces, COVID-19 Precautions Abound
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- As state economies across the U.S. are gradually reopening, workers are slowly returning to their workplaces, yet it is far from business as usual for most. Majorities of workers whose workplaces have employees on-site report that their employers are taking precautions to keep people from catching or spreading the coronavirus.
These safeguards include new or more frequent cleaning procedures at work, a measure 69% of workers report their employer is "always" taking. Additionally, 58% say their employer is always providing personal protective equipment, such as masks, gloves or face shields, and 54% say employers are enforcing a six-foot distance between employees and customers or other employees. Fewer, 41%, say their employers are always screening employees for cough or fever.
An additional 20% to 33% say each of these steps is happening "sometimes" at work. The measure least likely to be implemented is symptom checking, with 39% of workers saying their employer is never doing this.
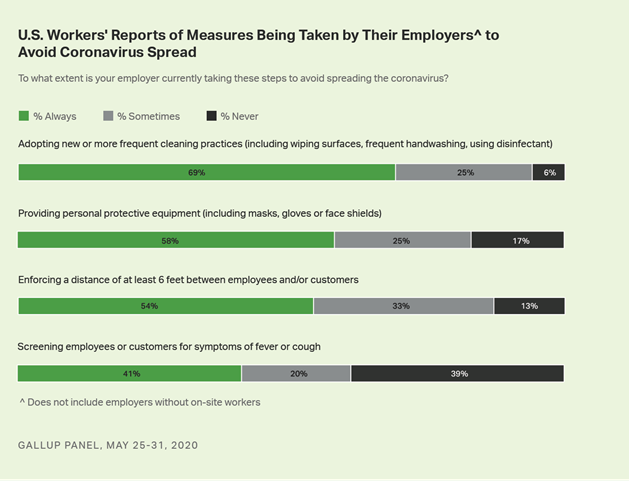
Stacked bar chart. Percentages of U.S. workers who say their employers with on-site staff are taking four specific actions to avoid catching or spreading the coronavirus. Sixty-nine percent are always adopting new or more frequent cleaning practices; 58% are always providing personal protective equipment; and 54% are always enforcing at least a six-foot distance between workers and customers or other workers. Fewer, 41% are always screening for fever or cough, but 20% are doing this sometimes. Data are from May 25-31, 2020.
Gallup has been tracking full- and part-time U.S. workers' activity and attitudes amid the COVID-19 pandemic using its online, probability-based panel survey since March. Between mid-April and late May, there has been a seven-percentage-point uptick in workers reporting at least some employees are working on-site at their workplaces.
U.S. Workers Increasingly Returning to Workplaces
To what extent are employees currently working on-site at your place of work?
|
Apr
13-May 3 |
May 4-31 |
|
|
% |
% |
|
|
All or nearly all employees |
28 |
33 |
|
Some employees |
17 |
19 |
|
Very few employees |
36 |
31 |
|
No employees |
16 |
14 |
|
GALLUP PANEL, 2020 |
||
Effects of and Concern About the Coronavirus in Workplace
With more workers returning to their workplaces in May, the latest survey, conducted May 25-31, finds nearly three-quarters of employed U.S. adults saying the coronavirus is having a very (23%) or somewhat (50%) negative effect on their workplace.
Even as workers may recognize the economic pressure on their employer to reopen, many also fear for their own personal safety. Nearly half are concerned -- either very (13%) or moderately (33%) -- about being exposed to the coronavirus at work. At the same time, 29% are not too concerned and 25% not at all concerned.
A separate item in the survey finds 25% of U.S. workers "strongly agree" that they can now return to work safely; fewer, 20%, "strongly disagree."
Workers' Actions to Avoid COVID-19 Spread
Apart from the steps employers are taking, majorities of workers are complying or taking matters into their own hands to avoid catching or spreading the virus. Two-thirds (67%) report they are adopting new or more frequent cleaning practices all the time at work; 59% are always trying to maintain at least a six-foot distance between themselves and other employees or customers; and 54% are always using personal protective equipment.
Fewer, 43%, are working remotely all the time, but 23% are doing this sometimes.
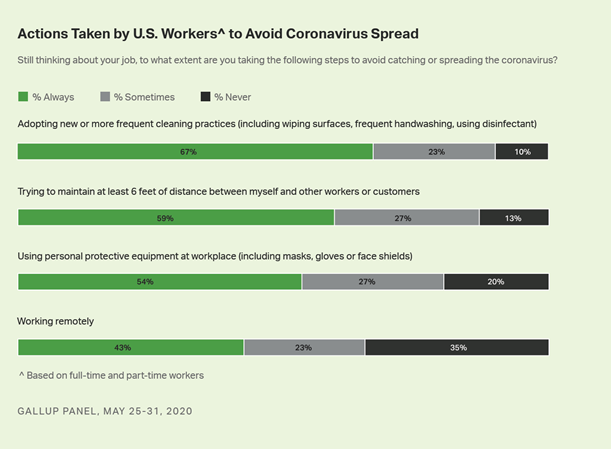
Stacked bar chart. Percentages of U.S. workers who are taking four specific actions to avoid catching or spreading the coronavirus. Sixty-seven percent are always adopting new or more frequent cleaning practices; 59% are always trying to maintain at least a six-foot distance between themselves and others; and 54% are always using personal protective equipment. Fewer, 43% are always working remotely, but 23% are doing this sometimes. Data are from May 25-31, 2020.
Bottom Line
As businesses nationwide wade cautiously into reopening their workplaces, nearly half of workers say they are concerned about exposure to COVID-19 at work. Employers and workers are taking extra precautions to avoid spreading the virus and prevent another deadly wave of infections in the U.S. The ability of such actions to prevent a second wave of coronavirus infections will help determine the pace and extent to which society reopens. Even after a vaccine is developed and coronavirus infections dwindle, the memory of people's vulnerability to infectious diseases may make some of these changes a permanent part of life.
(Gallup USA)
June 08, 2020
Source: https://news.gallup.com/poll/312461/amid-slow-return-workplaces-covid-precautions-abound.aspx
642-43-19/Poll
Social Factors Most Challenging in COVID-19 Distance Learning
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- The 2019-2020 academic year is ending in a way no one could have imagined, with classes being taught virtually and many parents serving as their child's primary instructor as schools are closed because of the coronavirus pandemic. Asked to rate the various challenges they've faced with remote learning, parents are more likely to identify difficulties they or their child has had in adjusting to virtual learning as major challenges than technical or resource issues.
Forty-five percent say their children being separated from classmates and teachers has been a major challenge for their family, and 44% say the same about their child's attention span and motivation. Also, 43% of working parents say balancing a job and helping kids with school has been a major challenge for them.
Twenty-eight percent of parents say teaching their child in a way they can learn has been a major challenge, while relatively few say the same about technical issues with the computer or internet (10%) or difficulty accessing educational resources (4%).
Separation, Motivation and Balancing Work and Teaching Have Been U.S. Families' Biggest Challenges With Remote Learning
How much of a challenge have each of the following been in terms of remote/distance learning for your [oldest/youngest] child?
|
Major
challenge |
Minor
challenge |
Not
a challenge |
|
|
% |
% |
% |
|
|
Being separated from classmates and teachers |
45 |
41 |
14 |
|
Your child's attention span or motivation |
44 |
34 |
22 |
|
Having to balance a job and helping kids with school ^ |
43 |
29 |
28 |
|
Knowing how to teach your child in ways they can learn |
28 |
40 |
32 |
|
Technical issues with the computer or internet |
10 |
33 |
58 |
|
Inability to access educational websites or resources |
4 |
29 |
67 |
|
^ Asked of employed parents |
|||
|
GALLUP PANEL, MAY 11-24, 2020 |
|||
The results are based on interviews with more than 1,200 parents of children in grades kindergarten through 12 whose school is closed to in-person instruction. Ninety-seven percent of parents say their child's school is currently closed. The sample is drawn from Gallup's probability-based online panel.
Younger parents -- those under age 45 -- are significantly more likely than older parents to say child attention span or motivation is a major challenge, 50% to 33%. Presumably, this is because younger parents tend to have younger children who have shorter attention spans and require more hands-on instruction.
Additionally, younger parents (53%) who are employed are more than twice as likely as older working parents (24%) to say balancing work and school has been a major challenge for their family.
Parents Rate Schools Positively for Handling Distance Learning
More than seven in 10 parents rate the job their school is doing with various aspects of COVID-19 distance learning positively, with roughly one-third saying the school is doing an excellent job in each area.
Seventy-seven percent say their school is doing an excellent or good job of making teachers available to answer questions about schoolwork, while slightly fewer say the same about providing students the materials and equipment they need to do their schoolwork, communication from the superintendent and principal about distance learning, and communication from teachers about assignments.
U.S. Parents Positive About How Child's School Is Handling Distance Learning
How would you rate the job your [oldest/youngest] child's school is doing in each of the following areas?
|
Excellent |
Good |
Only
fair |
Poor |
|
|
% |
% |
% |
% |
|
|
Teachers being available to answer questions you have |
39 |
38 |
20 |
4 |
|
Communication about the distance learning program from the superintendent and/or principal |
35 |
36 |
22 |
7 |
|
Providing the materials and equipment my child needs to do the schoolwork |
33 |
42 |
19 |
5 |
|
Communication about specific assignments from teachers |
31 |
41 |
20 |
8 |
|
GALLUP PANEL, MAY 11-24, 2020 |
||||
Mothers are more likely than fathers to say their child's school is doing an excellent job in each of these areas, and younger parents are more likely than older parents to say the same.
Implications
The 2019-2020 school year has brought unprecedented disruption to schools amid the coronavirus pandemic, which forced most U.S. schools to close in March. For the most part, parents believe their child's school has met the challenge well. Still, despite the best efforts of schools, distance learning presents practical challenges for parents and students. Being isolated from classmates and teachers, inspiring motivation in children to complete their assignments, and balancing teaching with a paying job are the biggest challenges.
With the beginning of the 2020-2021 academic year less than three months away, schools are still developing plans for what instruction will look like. The coronavirus continues to threaten public health, so it remains to be seen how much teaching and learning will be done in the traditional classroom setting versus online in the coming school year.
(Gallup USA)
June 12, 2020
Source: https://news.gallup.com/poll/312566/social-factors-challenging-covid-distance-learning.aspx
AUSTRALIA
642-43-20/Poll
Awareness of buy-now-pay-later services Afterpay and Zip soars to over 12.3 million Australians
The latest Roy Morgan Digital Payments Report shows over 12.3 million Australians (59%) are now aware of buy-now-pay-later services such as Afterpay and Zip – up 22.1% points in only 18 months.
Afterpay is the clear market leader with a majority of 55.8% of Australians aware of the service in the year to March 2020, up by 22% points since September 2018.
Main rival Zip is also making a significant impression on the Australian marketplace with over a third of Australians (35.2%) now aware of Zip – almost doubling awareness of the service in only 18 months.
The rising awareness of buy-now-pay-later services comes as the share prices of Afterpay, Zip and smaller rivals has soared during the COVID-19 induced shut-downs. The Afterpay share price increased by over 500% since a low of only $8 in late March and the share price of Zip was up over 50% last week alone.
The COVID-19 pandemic hit Australians hard in mid-March as shutdowns were enforced across the country however as the economy is progressively re-opened there are signs the impact on our way of life will provide an enduring benefit to some businesses says Roy Morgan CEO Michele Levine:
“Nearly three-fifths (59%)
of Australians are aware of buy-now-pay-later services such as Afterpay and Zip
and over one-in-ten (10.9%) now use these services. Digital payment services
have gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic as personal hygiene practices,
such as the way we handle money and pay for goods and services, have been put
in the spotlight.
“Afterpay and Zip are the
clear market leaders for buy-now-pay-later services but their early success in
Australia has attracted newer rivals. Newer local rivals include OpenPay,
Splitit Payments and Flexigroup which all offer buy-now-pay-later services and
indicate the increasingly competitive nature of the market.
“Australians aged 25-34 have
been the quickest to take to the buy-now-pay-later services with around
one-in-five in this age group using these new digital payment systems. However,
there are key differences between the two market leaders as Zip’s customer base
skews slightly older and their second strongest age group is those aged 35-49
whereas for Afterpay it is the under 25 market.
“There are other significant
differences between the types of customers both services attract that are drawn
out more fully in the Digital Payments Report. The report provides a detailed and in-depth
understanding of the Australians using not only buy-now-pay-later services but
also bill payment services, online payment platforms, contactless/cardless
mobile payments and wearable payment devices.”
These new digital payment findings are from Roy Morgan Single Source, Australia’s leading consumer survey, compiled by comprehensive interviews with a sample of over 1,000 Australians each week.
Buy-now-pay-later payments awareness trends: 2018-2020
(Roy Morgan)
June 09, 2020
Source: https://www.roymorgan.com/findings/8438-digital-payment-solutions-june-2020-202006090457
MULTICOUNTRY STUDIES
642-43-21/Poll
Do wealthy adults expect COVID-19 to cause recession?
Affluent Americans are
convinced the recession has already begun, whereas affluent Germans aren’t too
concerned about the economic effects of the spread of the virus
YouGov Affluence Perspective polling of wealthy adults* around the world reveals what concerns them most about the COVID-19 pandemic: looming recession, and whether local economies will be able to survive.
How concerned are the
wealthy about the virus itself?
Concern over the spread of the virus varies greatly across the countries examined in our latest survey, with European nations particularly split. At the top end are wealthy adults in Spain and Italy, 77% and 70% of whom respectively say they are either extremely or very concerned about the spread of COVID-19.
At the other end of the spectrum are France and Germany, where just 54% and 36% of wealthy adults respectively say they are concerned.
The UK sits somewhere in the middle, with two thirds (66%) of wealthy adults (those who have a household income of £100,000 or over) being concerned, similar to the US (69%).
Are we headed for recession?
The well-off think so
The pandemic has had a profound effect on the economies of the nations in its grip, and wealthy adults overwhelmingly predict a recession is on the horizon in their respective countries, if it has not already begun.
Canada (63%) and the UK (63%) are top for affluent adults who think a recession is near, with 32% in both countries think the recession brought on by the pandemic has already begun.
Affluent Germans, despite having the lowest concern for the virus spread by a wide margin, are expecting a recession (54%), a third (33%) think it is coming, and only 13% think the country will be spared an economic downturn.
Affluent adults in Spain and Italy are split over whether recessions in their countries have begun or have yet to come – compared to France and the United States where the majority of affluent adults say the recession has begun for them already.
One nation which bucks the trend is China, where most affluent adults (56%) do not believe the virus will lead the country into a recession, however a quarter (26%) do think one is on the horizon.
Confidence in the economy is
low among the rich
As well as prediction of recession, affluent adults across the world are also concerned about the ability of their local national economies to deal with the impacts of COVID-19.
Overall, Europeans are least confident in their respective economies, with 76% of affluent Italians saying they are not very or not confident at all their economy will cope. In neighbouring France, 69% of affluent adults say they are not confident in the French economy, to varying degrees.
Here in the UK, 60% of affluent adults are not confident to some extent that the economy will be able to cope, on par with the 63% who are expecting a recession in the near future.
One European nation upsetting this pattern is Germany, with only 29% of affluent Germans lacking confidence in their economy, compared to 30% who are confident their economy will be able to weather the COVID-19 storm. This is despite most affluent Germans also predicting a recession.
Two in five (41%) of affluent Chinese adults think the Chinese economy will also be able to cope with the pressures of the pandemic, making them the most confident nation of the countries examined in this survey. Only a quarter (24%) aren’t confident in the Chinese economy.
*Please note, the minimum household income that defines affluent adults in each country, all in local currencies :
UK: 100k
US: 200K
Canada: 150K
China: 250K
France: 100K
Spain: 90K
Italy: 90K
Germany: 100K
(YouGov)
June 11, 2020
642-43-22/Poll
How does COVID-19 spread? Global public belief in myths and theories
More people globally believe COVID-19 can live on surfaces for days over other theories. Theories about how the coronavirus can spread varies across 16 countries with some myths holding more prominence in regions like emerging markets, according to the latest survey by Ipsos.
In global poll of nearly 16,000 people conducted from May 28 to 31, more people believe COVID-19 can live up to three days on surfaces over all other theories presented with a majority of respondents saying this is true in 11 of the countries.
People in Canada and the United Kingdom (69%), Australia (66%), Spain and Brazil (61%) are most likely to believe this, while those in China (32%), India (26%), Germany and South Korea (25%) and Italy (24%) are most likely to say it’s false.
But at the same time, people are more divided on whether COVID-19 can be spread by boxes and packages sent from other countries where the virus is present.
Respondents in emerging markets of India (54%), South Africa (50%), Brazil (45%) and China (42%) are most likely to believe this, while those in Italy (66%), Russia (61%) and Germany (55%) are most likely to disagree.
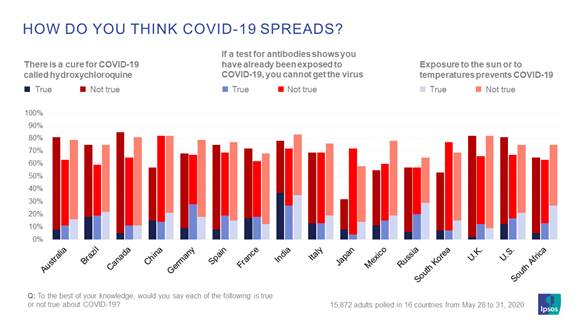
Exposure to drugs and
temperature
In terms of treatment for COVID-19, a majority of people in 11 countries do not believe that hydroxychloroquine is a cure for the virus with those in Canada and the U.K. (80%), Australia (73%), the United States (69%) and Spain (67%) most likely to say this is false.
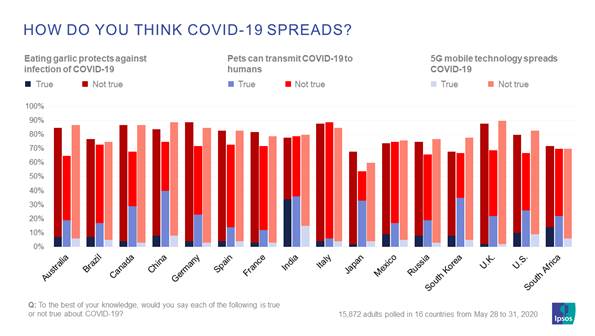
But people in India (37%) are mostly likely to believe the drug is a cure for the illness. Indians are also among the most likely to say that if a test for antibodies shows you have already been exposed to COVID-19, you cannot get the virus again. Those in Germany are also mostly like to say this is true at 28%, followed by 20% in Russia.
Meanwhile, those in South Korea (70%), Japan and China (68%) are most likely to say this is false.
When it comes to myths around exposure to the sun and temperatures to prevent contraction of COVID-19, people in India (35%), Russia (29%) and South Africa (27%) are most likely to believe this, while those in the U.K. (73%), Canada (70%) and Australia (63%) are most likely to say this is false.
Children, animals, food and
technology
In terms of human transmission, a majority of people in all the countries disagree with the theory that children cannot get COVID-19 with this sentiment highest in the U.K. (93%) and Canada (91%). Mexico is the only country where nearly one in five (17%) say this is true.
People are more divided on whether pets can transmit the virus to humans. Those in hard-hit countries like Italy (83%), France (60%) and Spain (59%), followed by Mexico (58%) and Brazil (56%) are most likely to say this is false, while more than a third of respondents in Asian nations of China (40%), India (36%), South Korea (35%) and Japan (33%) said it is true.
When it comes to what you can eat to prevent infection, people in India (34%) and South Africa (14%) are most likely to say that eating garlic protects against infection of COVID-19. But, a majority of people in 15 countries said this is not true.
Lastly, there is consensus that 5G mobile technology cannot spread COVID-19 with a majority in all 16 countries saying this is false. People in the U.K. (88%), Canada (84%) and Germany (82%) top the list on this.
(Ipsos MORI)
June 11, 2020